| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Rapid visualization of bacteria from a clinical sample such as a throat swab or sputum can be achieved through fluorescent antibody (FA) techniques that attach a fluorescent marker ( fluorogen ) to the constant region of an antibody, resulting in a reporter molecule that is quick to use, easy to see or measure, and able to bind to target markers with high specificity. We can also label cells, allowing us to precisely quantify particular subsets of cells or even purify these subsets for further research.
As with the enzyme assays, FA methods may be direct, in which a labeled mAb binds an antigen, or indirect, in which secondary polyclonal antibodies bind patient antibodies that react to a prepared antigen. Applications of these two methods were demonstrated in [link] . FA methods are also used in automated cell counting and sorting systems to enumerate or segregate labeled subpopulations of cells in a sample.
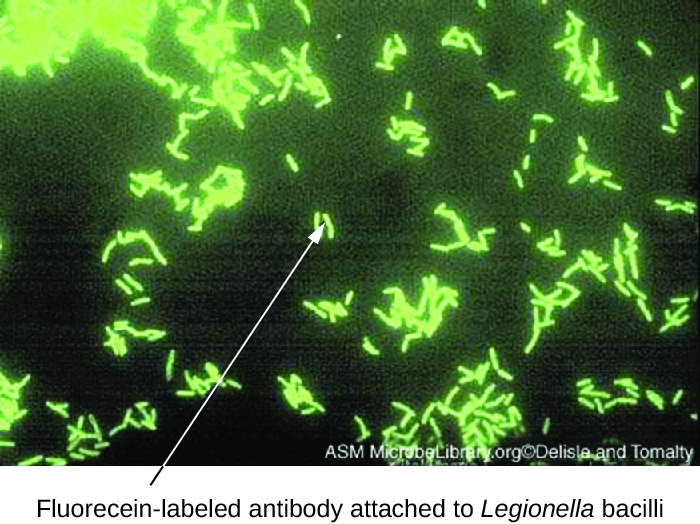
Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) tests use a fluorescently labeled mAb to bind and illuminate a target antigen. DFA tests are particularly useful for the rapid diagnosis of bacterial diseases. For example, fluorescence-labeled antibodies against Streptococcus pyogenes ( group A strep ) can be used to obtain a diagnosis of strep throat from a throat swab. The diagnosis is ready in a matter of minutes, and the patient can be started on antibiotics before even leaving the clinic. DFA techniques may also be used to diagnose pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae or Legionella pneumophila from sputum samples ( [link] ). The fluorescent antibodies bind to the bacteria on a microscope slide, allowing ready detection of the bacteria using a fluorescence microscope . Thus, the DFA technique is valuable for visualizing certain bacteria that are difficult to isolate or culture from patient samples.

Watch the animation on this page to review the procedures of the direct fluorescent antibody test.
Indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) tests ( [link] ) are used to look for antibodies in patient serum. For example, an IFA test for the diagnosis of syphilis uses T. pallidum cells isolated from a lab animal (the bacteria cannot be grown on lab media) and a smear prepared on a glass slide. Patient serum is spread over the smear and anti-treponemal antibodies, if present, are allowed to bind. The serum is washed off and a secondary antibody added. The secondary antibody is an antihuman immunoglobulin conjugated to a fluorogen . On examination, the T. pallidum bacteria will only be visible if they have been bound by the antibodies from the patient’s serum.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?