| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Two species of nematode worms are associated with hookworm infection . Both species are found in the Americas, Africa, and Asia. Necator americanus is found predominantly in the United States and Australia. Another species, Ancylostoma doudenale , is found in southern Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, and Asia.
The eggs of these species develop into larvae in soil contaminated by dog or cat feces. These larvae can penetrate the skin. After traveling through the venous circulation, they reach the lungs. When they are coughed up, they are then swallowed and can enter the intestine and develop into mature adults. At this stage, they attach to the wall of the intestine, where they feed on blood and can potentially cause anemia. Signs and symptoms include cough, an itchy rash, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. In children, hookworms can affect physical and cognitive growth.
Some hookworm species, such as Ancylostoma braziliense that is commonly found in animals such as cats and dogs, can penetrate human skin and migrate, causing cutaneous larva migrans , a skin disease caused by the larvae of hookworms. As they move across the skin, in the subcutaneous tissue, pruritic tracks appear ( [link] ).
The infection is diagnosed using microscopic examination of the stool, allowing for observation of eggs in the feces. Medications such as albendazole , mebendazole , and pyrantel pamoate are used as needed to treat systemic infection. In addition to systemic medication for symptoms associated with cutaneous larva migrans, topical thiabendazole is applied to the affected areas.
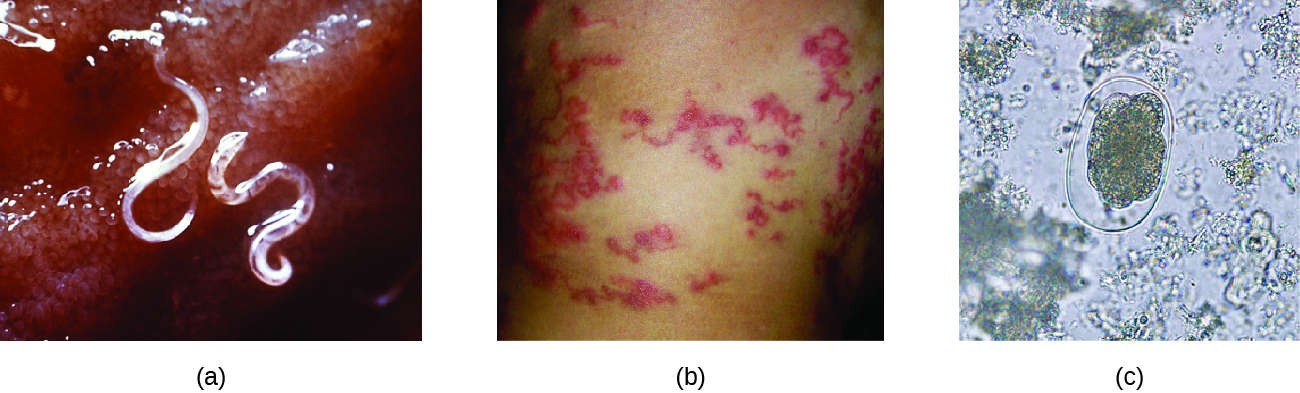
Strongyloidiasis is generally caused by Strongyloides stercoralis , a soil-transmitted helminth with both free-living and parasitic forms. In the parasitic form, the larvae of these nematodes generally penetrate the body through the skin, especially through bare feet, although transmission through organ transplantation or at facilities like day-care centers can also occur. When excreted in the stool, larvae can become free-living adults rather than developing into the parasitic form. These free-living worms reproduce, laying eggs that hatch into larvae that can develop into the parasitic form. In the parasitic life cycle, infective larvae enter the skin, generally through the feet. The larvae reach the circulatory system, which allows them to travel to the alveolar spaces of the lungs. They are transported to the pharynx where, like many other helminths, the infected patient coughs them up and swallows them again so that they return to the intestine . Once they reach the intestine, females live in the epithelium and produce eggs that develop asexually, unlike the free-living forms, which use sexual reproduction. The larvae may be excreted in the stool or can reinfect the host by entering the tissue of the intestines and skin around the anus, which can lead to chronic infections.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?