| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
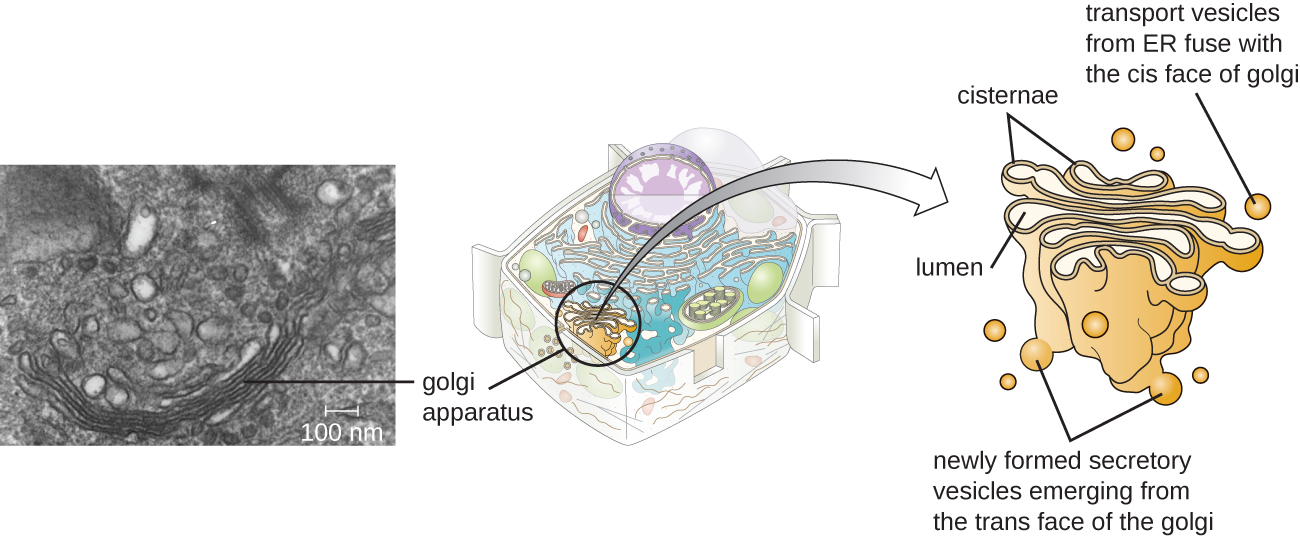
The Golgi apparatus was discovered within the endomembrane system in 1898 by Italian scientist Camillo Golgi (1843–1926), who developed a novel staining technique that showed stacked membrane structures within the cells of Plasmodium , the causative agent of malaria. The Golgi apparatus is composed of a series of membranous disks called dictyosomes, each having a single lipid bilayer, that are stacked together ( [link] ).
Enzymes in the Golgi apparatus modify lipids and proteins transported from the ER to the Golgi, often adding carbohydrate components to them, producing glycolipids, glycoproteins, or proteoglycans. Glycolipids and glycoproteins are often inserted into the plasma membrane and are important for signal recognition by other cells or infectious particles. Different types of cells can be distinguished from one another by the structure and arrangement of the glycolipids and glycoproteins contained in their plasma membranes. These glycolipids and glycoproteins commonly also serve as cell surface receptors.
Transport vesicles leaving the ER fuse with a Golgi apparatus on its receiving, or cis , face. The proteins are processed within the Golgi apparatus, and then additional transport vesicles containing the modified proteins and lipids pinch off from the Golgi apparatus on its outgoing, or trans , face. These outgoing vesicles move to and fuse with the plasma membrane or the membrane of other organelles.
Exocytosis is the process by which secretory vesicles (spherical membranous sacs) release their contents to the cell’s exterior ( [link] ). All cells have constitutive secretory pathways in which secretory vesicles transport soluble proteins that are released from the cell continually (constitutively). Certain specialized cells also have regulated secretory pathways , which are used to store soluble proteins in secretory vesicles. Regulated secretion involves substances that are only released in response to certain events or signals. For example, certain cells of the human immune system (e.g., mast cells) secrete histamine in response to the presence of foreign objects or pathogens in the body. Histamine is a compound that triggers various mechanisms used by the immune system to eliminate pathogens.
In the 1960s, Belgian scientist Christian de Duve (1917–2013) discovered lysosomes , membrane-bound organelles of the endomembrane system that contain digestive enzymes. Certain types of eukaryotic cells use lysosomes to break down various particles, such as food, damaged organelles or cellular debris, microorganisms, or immune complexes. Compartmentalization of the digestive enzymes within the lysosome allows the cell to efficiently digest matter without harming the cytoplasmic components of the cell.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?