| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
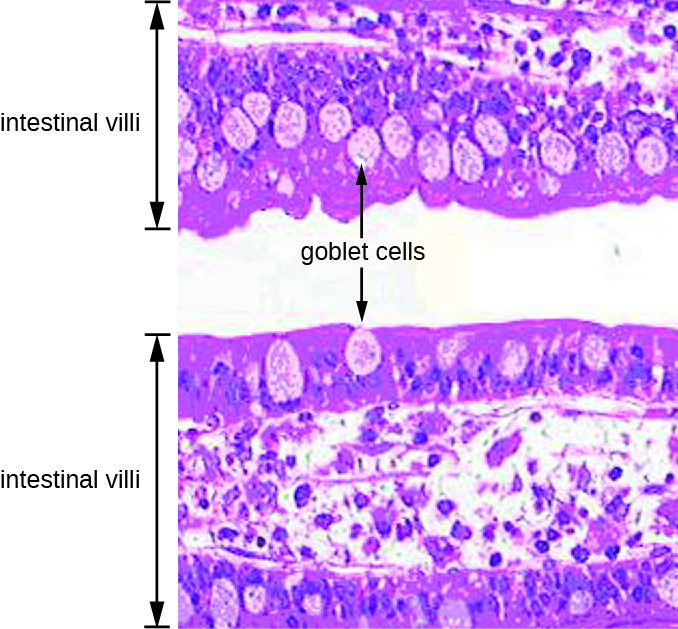
Despite numerous defense mechanisms that protect against infection, all parts of the digestive tract can become sites of infection or intoxication. The term food poisoning is sometimes used as a catch-all for GI infections and intoxications, but not all forms of GI disease originate with foodborne pathogens or toxins.
In the mouth, fermentation by anaerobic microbes produces acids that damage the teeth and gums. This can lead to tooth decay, cavities, and periodontal disease , a condition characterized by chronic inflammation and erosion of the gums . Additionally, some pathogens can cause infections of the mucosa, glands, and other structures in the mouth, resulting in inflammation, sores, cankers, and other lesions. An open sore in the mouth or GI tract is typically called an ulcer .
Infections and intoxications of the lower GI tract often produce symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, aches, and fever. In some cases, vomiting and diarrhea may cause severe dehydration and other complications that can become serious or fatal. Various clinical terms are used to describe gastrointestinal symptoms. For example, gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining that results in swelling and enteritis refers to inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. When the inflammation involves both the stomach lining and the intestinal lining, the condition is called gastroenteritis . Inflammation of the liver is called hepatitis . Inflammation of the colon, called colitis , commonly occurs in cases of food intoxication. Because an inflamed colon does not reabsorb water as effectively as it normally does, stools become watery, causing diarrhea. Damage to the epithelial cells of the colon can also cause bleeding and excess mucus to appear in watery stools, a condition called dysentery .
The part of the gastrointestinal tract with the largest natural microbiota is the _________.
Large intestine or colon
How does the diarrhea caused by dysentery differ from other types of diarrhea?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?