| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Phylum Spirochaetes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Genus | Species | Related Diseases |
| Spirochaetia | Borrelia | burgdorferi | Lyme disease |
| Borrelia | hermsii | Tick-borne relapsing fever | |
| Borrelia | recurrentis | Louse-borne relapsing fever | |
| Leptospira | interrogans | Leptospirosis | |
| Treponema | pallidum | Syphilis, bejel, pinta, yaws |
| Phylum Tenericutes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Genus | Species | Related Diseases |
| Mollicutes | Mycoplasma | genitalium | Urethritis, cervicitis |
| Mycoplasma | hominis | Pelvic inflammatory disease, bacterial vaginosis | |
| Mycoplasma | pneumoniae | Mycoplasma pneumonia | |
| Ureaplasma | urealyticum | Urethritis, fetal infections |
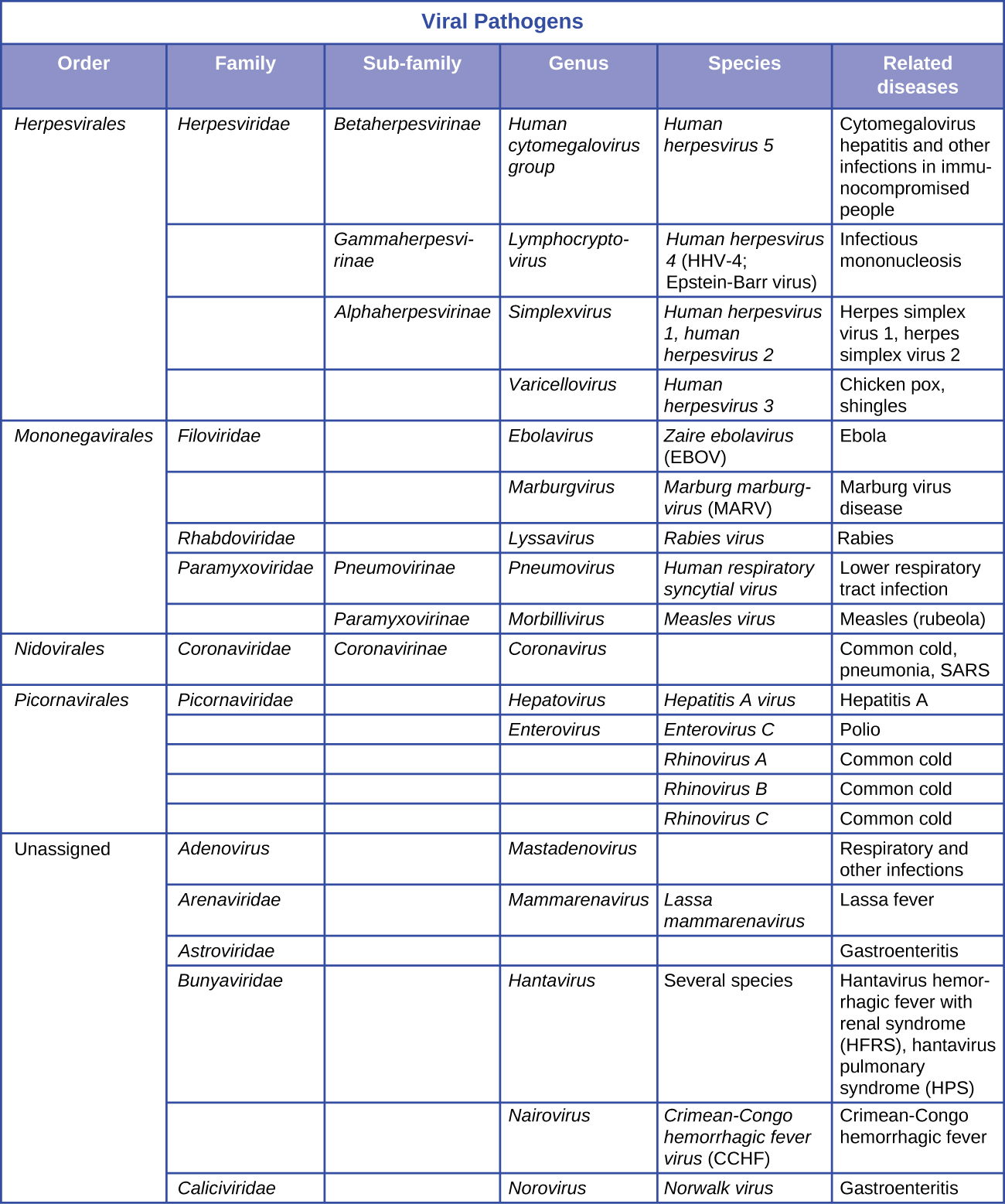
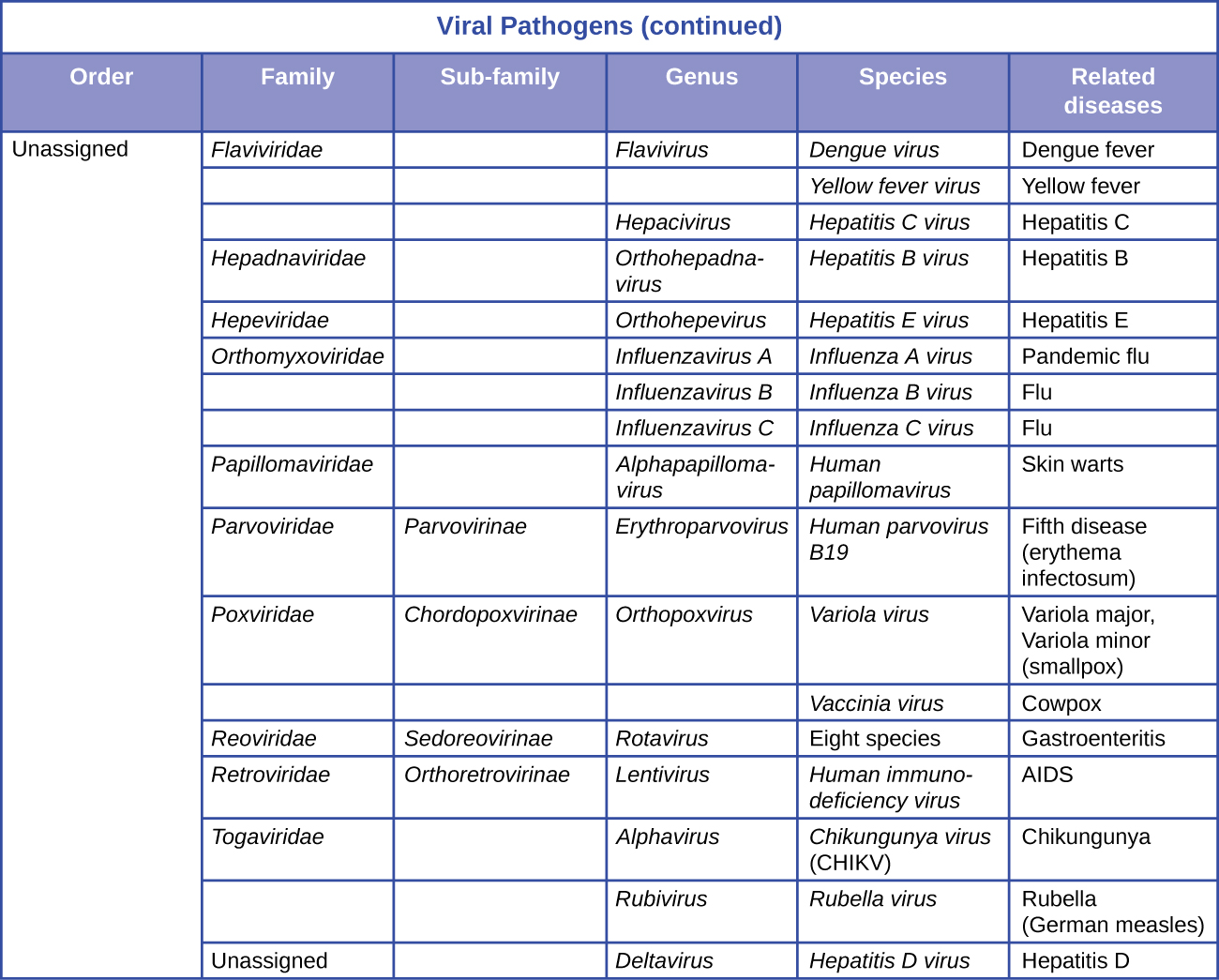
There are several classification systems for viruses. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) is the international scientific body responsible for the rules of viral classification. The ICTV system used here groups viruses based on genetic similarity and presumed monophyly. The viral classification system is separate from the classification system for cellular organisms. The ICTV system groups viruses within seven orders, which contain related families. There is, presently, a large number of unassigned families with unknown affinities to the seven orders. Three of these orders infect only Eubacteria, Archaea, or plants and do not appear in this table. Some families may be divided into subfamilies. There are also many unassigned genera. Like all taxonomies, viral taxonomy is in constant flux. The latest complete species list and classification can be obtained on the ICTV website. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. “ICTV Master Species List.” http://talk.ictvonline.org/files/ictv_documents/m/msl/default.aspx
The Fungi are one of the kingdoms of the domain Eukarya. Fungi are most closely related to the animals and a few other small groups and more distantly related to the plants and other groups that formerly were categorized as protist. At present, the Fungi are divided into seven phyla (or divisions, a hold over from when fungi were studied with plants), but there are uncertainties about some relationships. D. S. Hibbett et al. “A Higher-level Phylogenetic Classification of the Fungi.” Mycological Research 111 no. 5 (2007):509–547. Many groups of fungi, particularly those that were formerly classified in the phylum Zygomycota, which was not monophyletic, have uncertain relationships to the other fungi. The one species listed in this table that falls into this category is Rhizopus arrhizus. Fungal names are governed by the International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants, J. McNeill et al. International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Melbourne Code) . Oberreifenerg, Germany. Koeltz Scientific Books; 2012. http://www.iapt-taxon.org/nomen/main.php? but the International Commission on the Taxonomy of Fungi (ICTF) also promotes taxonomic work on fungi. One activity of the ICTF is publicizing name changes for medically and otherwise important fungal species. Many species that formerly had two names (one for the sexual form and one for the asexual form) are now being brought together under one name.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?