| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
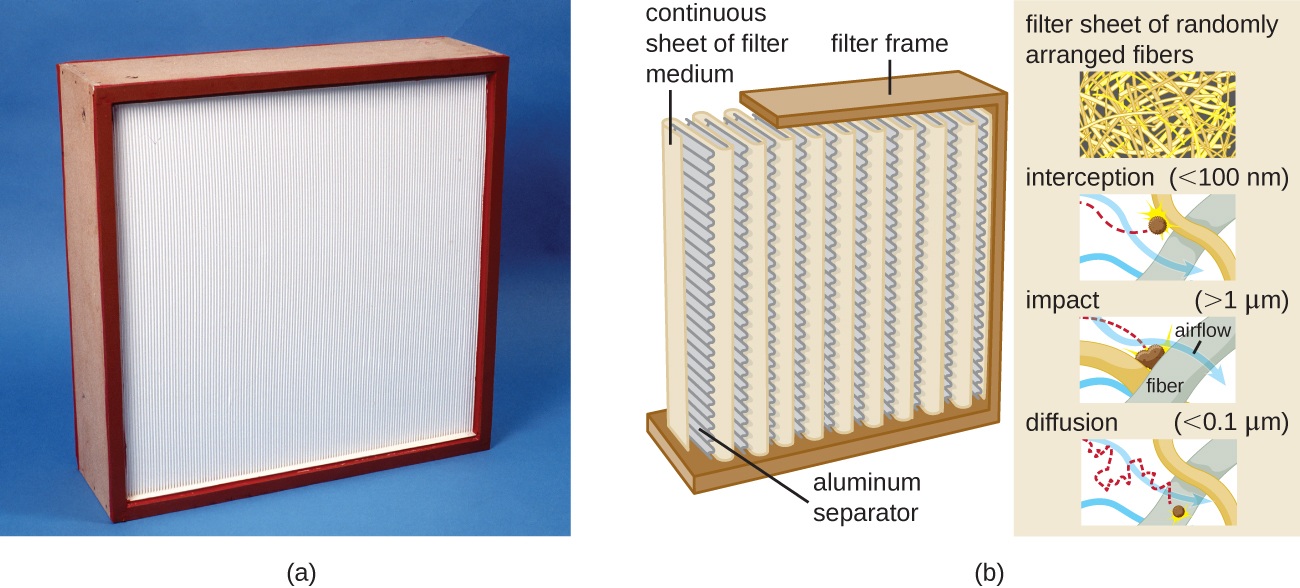
Biological safety cabinets are a good example of the use of HEPA filters. HEPA filters in biological safety cabinet s (BSCs) are used to remove particulates in the air either entering the cabinet (air intake), leaving the cabinet (air exhaust), or treating both the intake and exhaust. Use of an air-intake HEPA filter prevents environmental contaminants from entering the BSC, creating a clean area for handling biological materials. Use of an air-exhaust HEPA filter prevents laboratory pathogens from contaminating the laboratory, thus maintaining a safe work area for laboratory personnel.
There are three classes of BSCs: I, II, and III. Each class is designed to provide a different level of protection for laboratory personnel and the environment; BSC II and III are also designed to protect the materials or devices in the cabinet. [link] summarizes the level of safety provided by each class of BSC for each BSL.
| Biological Risks and BSCs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Risk Assessed | BSC Class | Protection of Personnel | Protection of Environment | Protection of Product |
| BSL-1, BSL-2, BSL-3 | I | Yes | Yes | No |
| BSL-1, BSL-2, BSL-3 | II | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| BSL-4 | III; II when used in suit room with suit | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Class I BSCs protect laboratory workers and the environment from a low to moderate risk for exposure to biological agents used in the laboratory. Air is drawn into the cabinet and then filtered before exiting through the building’s exhaust system. Class II BSCs use directional air flow and partial barrier systems to contain infectious agents. Class III BSCs are designed for working with highly infectious agents like those used in BSL-4 laboratories. They are gas tight, and materials entering or exiting the cabinet must be passed through a double-door system, allowing the intervening space to be decontaminated between uses. All air is passed through one or two HEPA filters and an air incineration system before being exhausted directly to the outdoors (not through the building’s exhaust system). Personnel can manipulate materials inside the Class III cabinet by using long rubber gloves sealed to the cabinet.
This video shows how BSCs are designed and explains how they protect personnel, the environment, and the product.
HEPA filters are also commonly used in hospitals and surgical suites to prevent contamination and the spread of airborne microbes through ventilation systems. HEPA filtration systems may be designed for entire buildings or for individual rooms. For example, burn units, operating rooms, or isolation units may require special HEPA-filtration systems to remove opportunistic pathogens from the environment because patients in these rooms are particularly vulnerable to infection.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?