| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
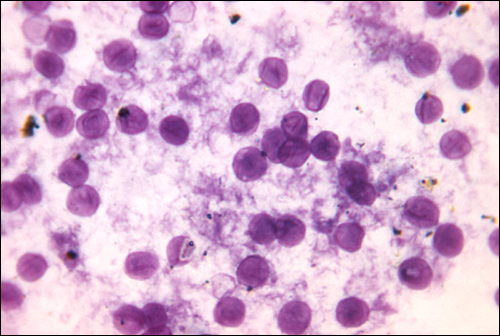
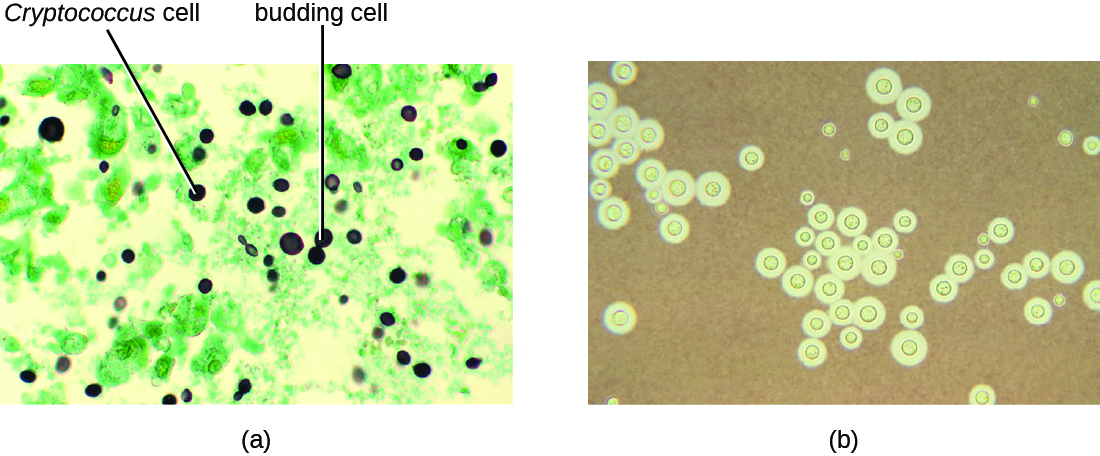
Infection by the encapsulated yeast Cryptococcus neoformans causes cryptococcosis . This fungus is ubiquitous in the soil and can be isolated from bird feces. Immunocompromised people are infected by inhaling basidiospores found in aerosols. The thick polysaccharide capsule surrounding these microbes enables them to avoid clearance by the alveolar macrophage. Initial symptoms of infection include fever, fatigue, and a dry cough. In immunocompromised patients, pulmonary infections often disseminate to the brain. The resulting meningitis produces headaches, sensitivity to light, and confusion. Left untreated, such infections are often fatal.
Cryptococcus infections are often diagnosed based on microscopic examination of lung tissues or cerebrospinal fluids. India ink preparations ( [link] ) can be used to visualize the extensive capsules that surround the yeast cells. Serological tests are also available to confirm the diagnosis. Amphotericin B, in combination with flucytosine , is typically used for the initial treatment of pulmonary infections. Amphotericin B is a broad-spectrum antifungal drug that targets fungal cell membranes. It can also adversely impact host cells and produce side effects. For this reason, clinicians must carefully balance the risks and benefits of treatments in these patients. Because it is difficult to eradicate cryptococcal infections, patients usually need to take fluconazole for up to 6 months after treatment with amphotericin B and flucytosine to clear the fungus. Cryptococcal infections are more common in immunocompromised people, such as those with AIDS. These patients typically require life-long suppressive therapy to control this fungal infection.
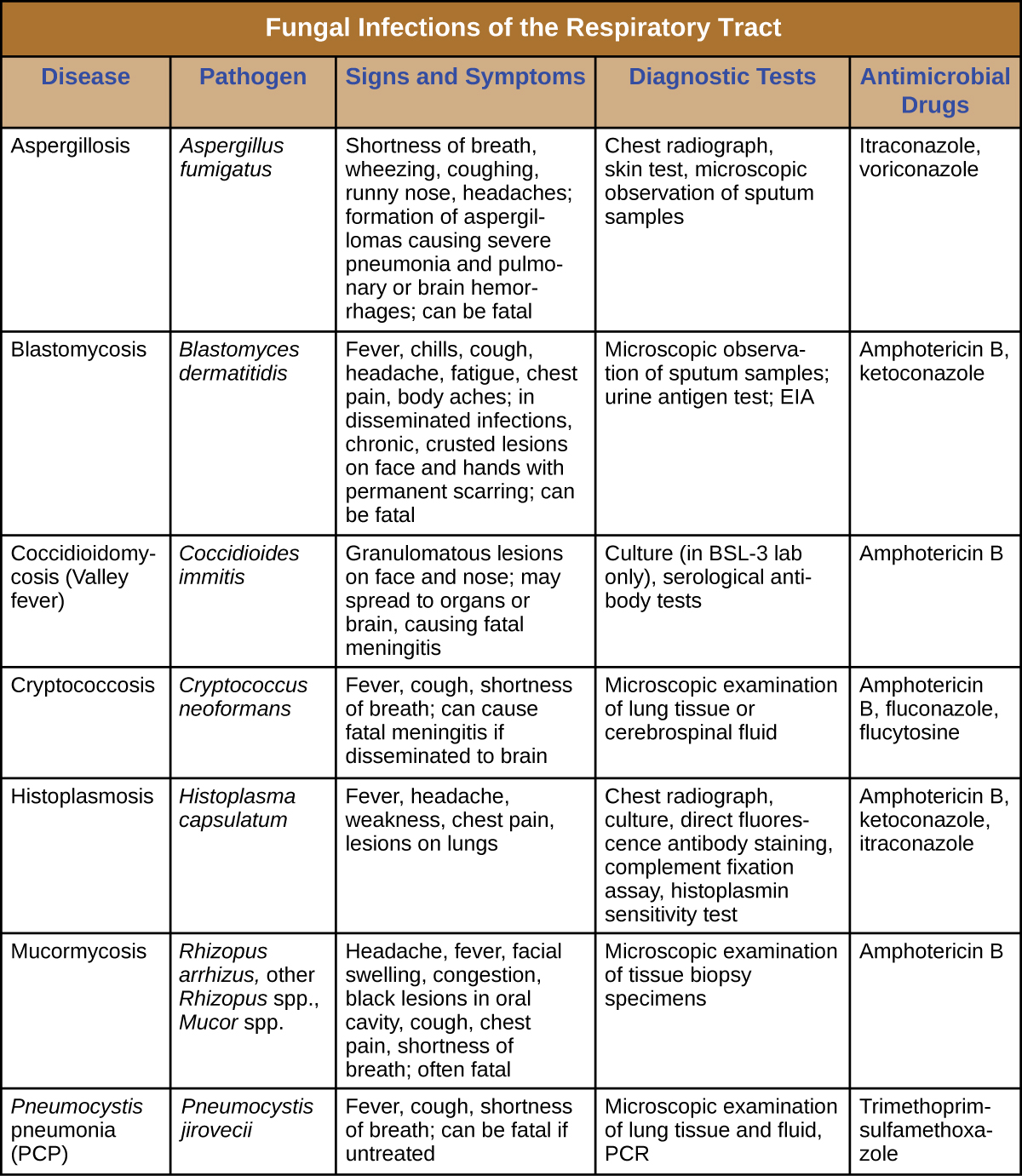
Most respiratory mycoses are caused by fungi that inhabit the environment. Such infections are generally transmitted via inhalation of fungal spores and cannot be transmitted between humans. In addition, healthy people are generally not susceptible to infection even when exposed; the fungi are only virulent enough to establish infection in patients with HIV, AIDS, or another condition that compromises the immune defenses. [link] summarizes the features of important respiratory mycoses.
In coccidioidomycosis, _______ containing many endospores form in the lungs.
spherules
In cryptococcosis, the main fungal virulence factor is the _______, which helps the pathogen avoid phagocytosis.
capsule
In some mycoses, fungal balls called _______ form in the lungs
aspergillomas
Most US cases of coccidioidomycosis occur in _______.
the desert southwest
Coccidioidomycosis may develop when Coccidioides immitis _______ are inhaled.
arthrospores
Which pulmonary fungal infection is most likely to be confused with tuberculosis? How can we discriminate between these two types of infection?
Compare and contrast aspergillosis and mucormycosis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?