| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
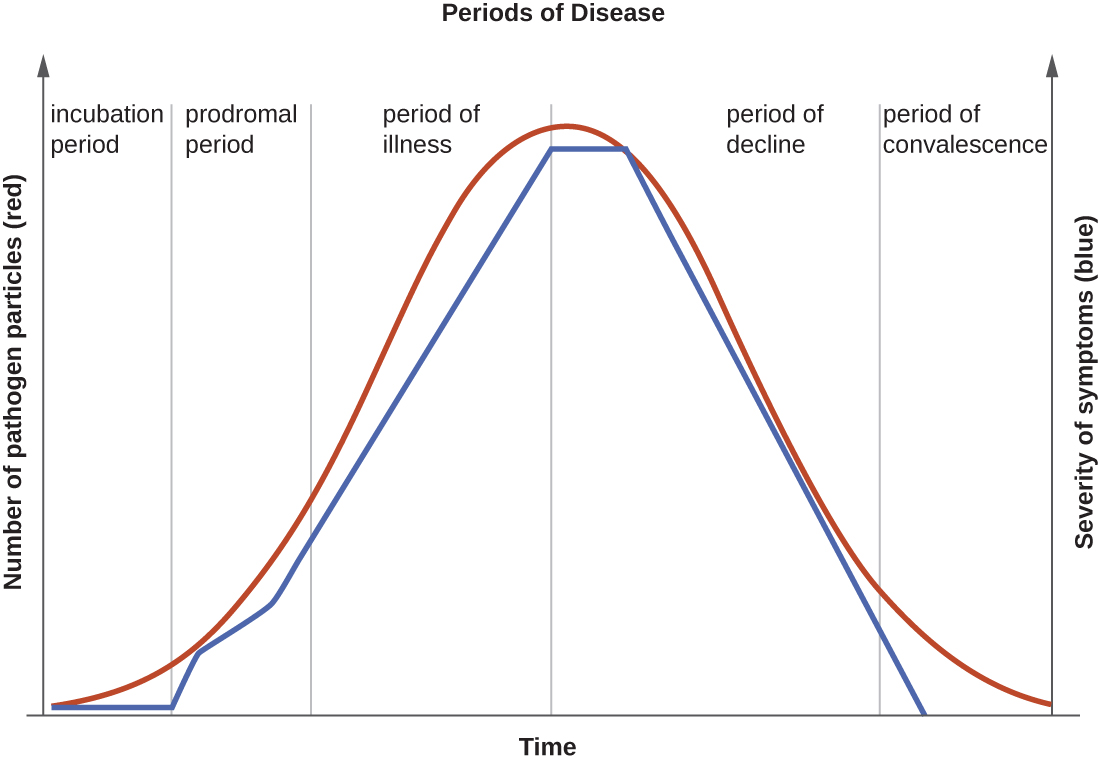
The prodromal period occurs after the incubation period. During this phase, the pathogen continues to multiply and the host begins to experience general signs and symptoms of illness, which typically result from activation of the immune system, such as fever, pain, soreness, swelling, or inflammation. Usually, such signs and symptoms are too general to indicate a particular disease. Following the prodromal period is the period of illness , during which the signs and symptoms of disease are most obvious and severe.
The period of illness is followed by the period of decline , during which the number of pathogen particles begins to decrease, and the signs and symptoms of illness begin to decline. However, during the decline period, patients may become susceptible to developing secondary infections because their immune systems have been weakened by the primary infection. The final period is known as the period of convalescence . During this stage, the patient generally returns to normal functions, although some diseases may inflict permanent damage that the body cannot fully repair.
Infectious diseases can be contagious during all five of the periods of disease. Which periods of disease are more likely to associated with transmissibility of an infection depends upon the disease, the pathogen, and the mechanisms by which the disease develops and progresses. For example, with meningitis (infection of the lining of brain), the periods of infectivity depend on the type of pathogen causing the infection. Patients with bacterial meningitis are contagious during the incubation period for up to a week before the onset of the prodromal period, whereas patients with viral meningitis become contagious when the first signs and symptoms of the prodromal period appear. With many viral diseases associated with rashes (e.g., chickenpox , measles , rubella , roseola ), patients are contagious during the incubation period up to a week before the rash develops. In contrast, with many respiratory infections (e.g., colds, influenza , diphtheria , strep throat , and pertussis ) the patient becomes contagious with the onset of the prodromal period. Depending upon the pathogen, the disease, and the individual infected, transmission can still occur during the periods of decline, convalescence, and even long after signs and symptoms of the disease disappear. For example, an individual recovering from a diarrheal disease may continue to carry and shed the pathogen in feces for some time, posing a risk of transmission to others through direct contact or indirect contact (e.g., through contaminated objects or food).
The duration of the period of illness can vary greatly, depending on the pathogen, effectiveness of the immune response in the host, and any medical treatment received. For an acute disease , pathologic changes occur over a relatively short time (e.g., hours, days, or a few weeks) and involve a rapid onset of disease conditions. For example, influenza (caused by Influenzavirus) is considered an acute disease because the incubation period is approximately 1–2 days. Infected individuals can spread influenza to others for approximately 5 days after becoming ill. After approximately 1 week, individuals enter the period of decline.
For a chronic disease , pathologic changes can occur over longer time spans (e.g., months, years, or a lifetime). For example, chronic gastritis (inflammation of the lining of the stomach) is caused by the gram-negative bacterium Helicobacter pylori . H. pylori is able to colonize the stomach and persist in its highly acidic environment by producing the enzyme urease, which modifies the local acidity, allowing the bacteria to survive indefinitely. J.G. Kusters et al. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 19 no. 3 (2006):449–490. Consequently, H. pylori infections can recur indefinitely unless the infection is cleared using antibiotics. N.R. Salama et al. “Life in the Human Stomach: Persistence Strategies of the Bacterial Pathogen Helicobacter pylori .” Nature Reviews Microbiology 11 (2013):385–399. Hepatitis B virus can cause a chronic infection in some patients who do not eliminate the virus after the acute illness. A chronic infection with hepatitis B virus is characterized by the continued production of infectious virus for 6 months or longer after the acute infection, as measured by the presence of viral antigen in blood samples.
In latent disease s , as opposed to chronic infections, the causal pathogen goes dormant for extended periods of time with no active replication. Examples of diseases that go into a latent state after the acute infection include herpes (herpes simplex viruses [HSV-1 and HSV-2]), chickenpox ( varicella-zoster virus [VZV]), and mononucleosis ( Epstein-Barr virus [EBV]). HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV evade the host immune system by residing in a latent form within cells of the nervous system for long periods of time, but they can reactivate to become active infections during times of stress and immunosuppression. For example, an initial infection by VZV may result in a case of childhood chickenpox, followed by a long period of latency. The virus may reactivate decades later, causing episodes of shingles in adulthood. EBV goes into latency in B cells of the immune system and possibly epithelial cells; it can reactivate years later to produce B-cell lymphoma.
A difference between an acute disease and chronic disease is that chronic diseases have an extended period of __________.
illness
A person steps on a rusty nail and develops tetanus. In this case, the person has acquired a(n) __________ disease.
noncommunicable
Brian goes to the hospital after not feeling well for a week. He has a fever of 38 °C (100.4 °F) and complains of nausea and a constant migraine. Distinguish between the signs and symptoms of disease in Brian’s case.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?