| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
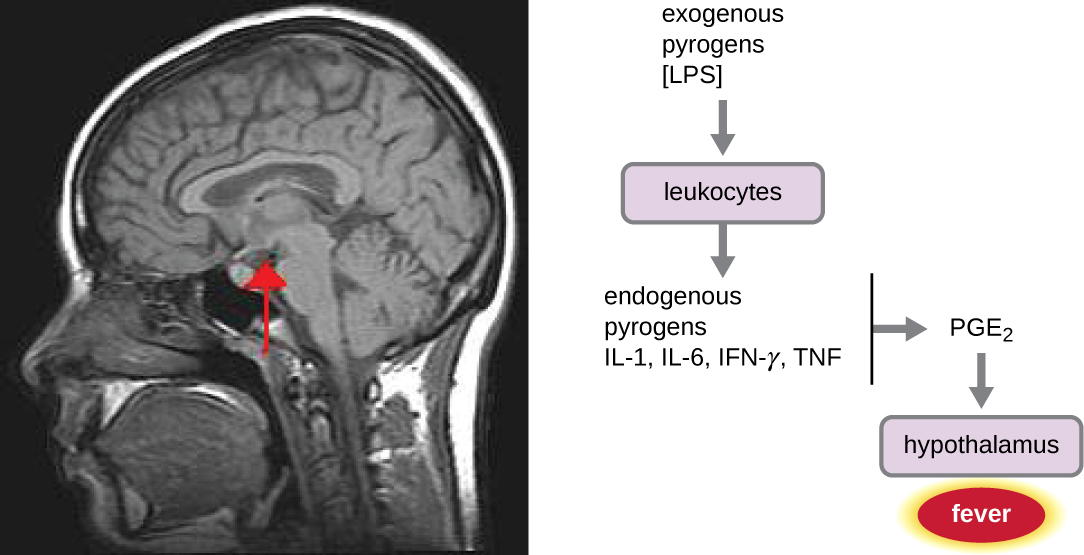
A fever is an inflammatory response that extends beyond the site of infection and affects the entire body, resulting in an overall increase in body temperature. Body temperature is normally regulated and maintained by the hypothalamus, an anatomical section of the brain that functions to maintain homeostasis in the body. However, certain bacterial or viral infections can result in the production of pyrogens , chemicals that effectively alter the “thermostat setting” of the hypothalamus to elevate body temperature and cause fever. Pyrogens may be exogenous or endogenous. For example, the endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS) , produced by gram-negative bacteria, is an exogenous pyrogen that may induce the leukocytes to release endogenous pyrogens such as interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). In a cascading effect, these molecules can then lead to the release of prostaglandin E2 (PGE 2 ) from other cells, resetting the hypothalamus to initiate fever ( [link] ).
Like other forms of inflammation, a fever enhances the innate immune defenses by stimulating leukocytes to kill pathogens. The rise in body temperature also may inhibit the growth of many pathogens since human pathogens are mesophiles with optimum growth occurring around 35 °C (95 °F). In addition, some studies suggest that fever may also stimulate release of iron-sequestering compounds from the liver, thereby starving out microbes that rely on iron for growth. N. Parrow et al. “Sequestration and Scavenging of Iron in Infection.” Infection and Immunity 81 no. 10 (2013):3503–3514
During fever , the skin may appear pale due to vasoconstriction of the blood vessels in the skin, which is mediated by the hypothalamus to divert blood flow away from extremities, minimizing the loss of heat and raising the core temperature. The hypothalamus will also stimulate shivering of muscles, another effective mechanism of generating heat and raising the core temperature.
The crisis phase occurs when the fever breaks. The hypothalamus stimulates vasodilation , resulting in a return of blood flow to the skin and a subsequent release of heat from the body. The hypothalamus also stimulates sweating, which cools the skin as the sweat evaporates.
Although a low-level fever may help an individual overcome an illness, in some instances, this immune response can be too strong, causing tissue and organ damage and, in severe cases, even death. The inflammatory response to bacterial superantigens is one scenario in which a life-threatening fever may develop. Superantigens are bacterial or viral proteins that can cause an excessive activation of T cells from the specific adaptive immune defense, as well as an excessive release of cytokines that overstimulates the inflammatory response. For example, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are capable of producing superantigens that cause toxic shock syndrome and scarlet fever , respectively. Both of these conditions can be associated with very high, life-threatening fevers in excess of 42 °C (108 °F).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?