| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Occasionally, certain types of inclusions are surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer embedded with protein. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) , which can be produced by species of Bacillus and Pseudomonas , is an example of an inclusion that displays this type of monolayer structure. Industrially, PHB has also been used as a source of biodegradable polymers for bioplastics. Several different types of inclusions are shown in [link] .
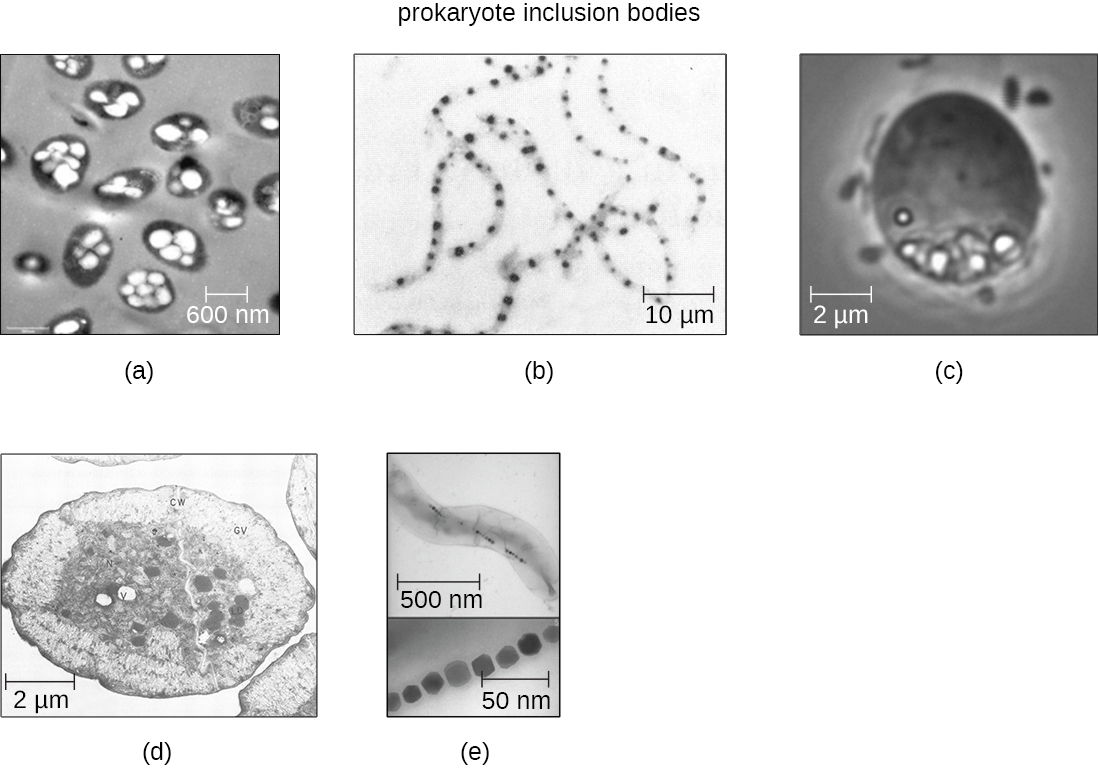
Some prokaryotic cells have other types of inclusions that serve purposes other than nutrient storage. For example, some prokaryotic cells produce gas vacuoles, accumulations of small, protein-lined vesicles of gas. These gas vacuoles allow the prokaryotic cells that synthesize them to alter their buoyancy so that they can adjust their location in the water column. Magnetotactic bacteria, such as Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum , contain magnetosomes , which are inclusions of magnetic iron oxide or iron sulfide surrounded by a lipid layer. These allow cells to align along a magnetic field, aiding their movement ( [link] ). Cyanobacteria such as Anabaena cylindrica and bacteria such as Halothiobacillus neapolitanus produce carboxysome inclusions. Carboxysomes are composed of outer shells of thousands of protein subunits. Their interior is filled with ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) and carbonic anhydrase. Both of these compounds are used for carbon metabolism. Some prokaryotic cells also possess carboxysomes that sequester functionally related enzymes in one location. These structures are considered proto-organelles because they compartmentalize important compounds or chemical reactions, much like many eukaryotic organelles.
Bacterial cells are generally observed as vegetative cells , but some genera of bacteria have the ability to form endospores , structures that essentially protect the bacterial genome in a dormant state when environmental conditions are unfavorable. Endospores (not to be confused with the reproductive spores formed by fungi) allow some bacterial cells to survive long periods without food or water, as well as exposure to chemicals, extreme temperatures, and even radiation. [link] compares the characteristics of vegetative cells and endospores.
| Characteristics of Vegetative Cells versus Endospores | |
|---|---|
| Vegetative Cells | Endospores |
| Sensitive to extreme temperatures and radiation | Resistant to extreme temperatures and radiation |
| Gram-positive | Do not absorb Gram stain, only special endospore stains (see Staining Microscopic Specimens ) |
| Normal water content and enzymatic activity | Dehydrated; no metabolic activity |
| Capable of active growth and metabolism | Dormant; no growth or metabolic activity |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?