| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In eukaryotes, initiation complex formation is similar, with the following differences:
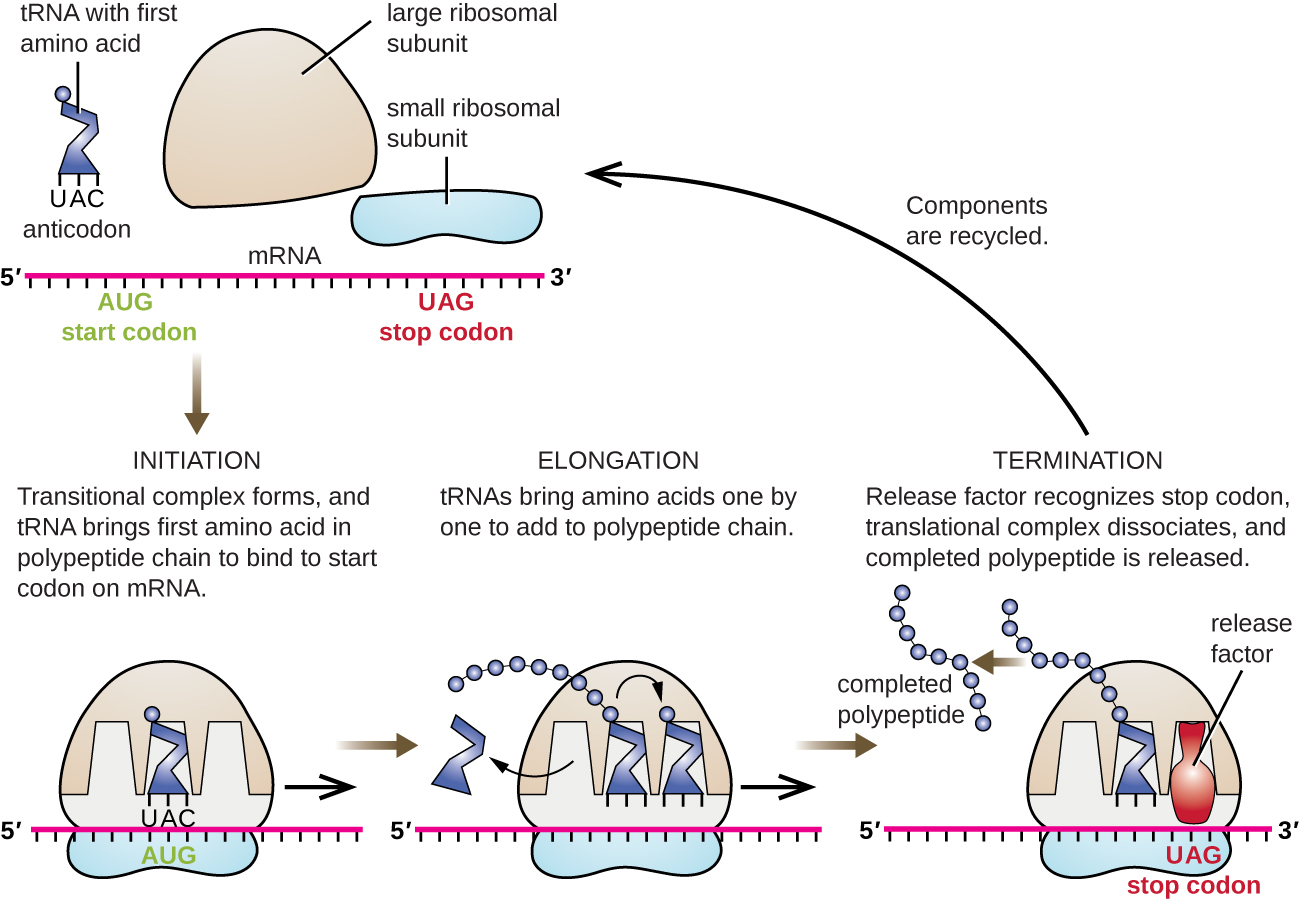
In prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the basics of elongation of translation are the same. In E. coli , the binding of the 50S ribosomal subunit to produce the intact ribosome forms three functionally important ribosomal sites: The A (aminoacyl) site binds incoming charged aminoacyl tRNAs. The P (peptidyl) site binds charged tRNAs carrying amino acids that have formed peptide bonds with the growing polypeptide chain but have not yet dissociated from their corresponding tRNA. The E (exit) site releases dissociated tRNAs so that they can be recharged with free amino acids. There is one notable exception to this assembly line of tRNAs: During initiation complex formation, bacterial fMet−tRNA fMet or eukaryotic Met-tRNAi enters the P site directly without first entering the A site, providing a free A site ready to accept the tRNA corresponding to the first codon after the AUG.
Elongation proceeds with single-codon movements of the ribosome each called a translocation event. During each translocation event, the charged tRNAs enter at the A site, then shift to the P site, and then finally to the E site for removal. Ribosomal movements, or steps, are induced by conformational changes that advance the ribosome by three bases in the 3’ direction. Peptide bonds form between the amino group of the amino acid attached to the A-site tRNA and the carboxyl group of the amino acid attached to the P-site tRNA. The formation of each peptide bond is catalyzed by peptidyl transferase , an RNA-based ribozyme that is integrated into the 50S ribosomal subunit. The amino acid bound to the P-site tRNA is also linked to the growing polypeptide chain. As the ribosome steps across the mRNA, the former P-site tRNA enters the E site, detaches from the amino acid, and is expelled. Several of the steps during elongation, including binding of a charged aminoacyl tRNA to the A site and translocation, require energy derived from GTP hydrolysis, which is catalyzed by specific elongation factors. Amazingly, the E. coli translation apparatus takes only 0.05 seconds to add each amino acid, meaning that a 200 amino-acid protein can be translated in just 10 seconds.
The termination of translation occurs when a nonsense codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered for which there is no complementary tRNA. On aligning with the A site, these nonsense codons are recognized by release factors in prokaryotes and eukaryotes that result in the P-site amino acid detaching from its tRNA, releasing the newly made polypeptide. The small and large ribosomal subunits dissociate from the mRNA and from each other; they are recruited almost immediately into another translation init iation complex.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?