| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The microbial community of the nasopharynx is extremely diverse and harbors many opportunistic pathogens, so it is perhaps not surprising that infections leading to rhinitis and sinusitis have many possible causes. These conditions often occur as secondary infections after a viral infection, which effectively compromises the immune defenses and allows the opportunistic bacteria to establish themselves. Bacterial sinusitis involves infection and inflammation within the paranasal sinuses. Because bacterial sinusitis rarely occurs without rhinitis, the preferred term is rhinosinusitis . The most common causes of bacterial rhinosinusitis are similar to those for AOM, including S. pneumoniae , H. influenzae , and M. catarrhalis .
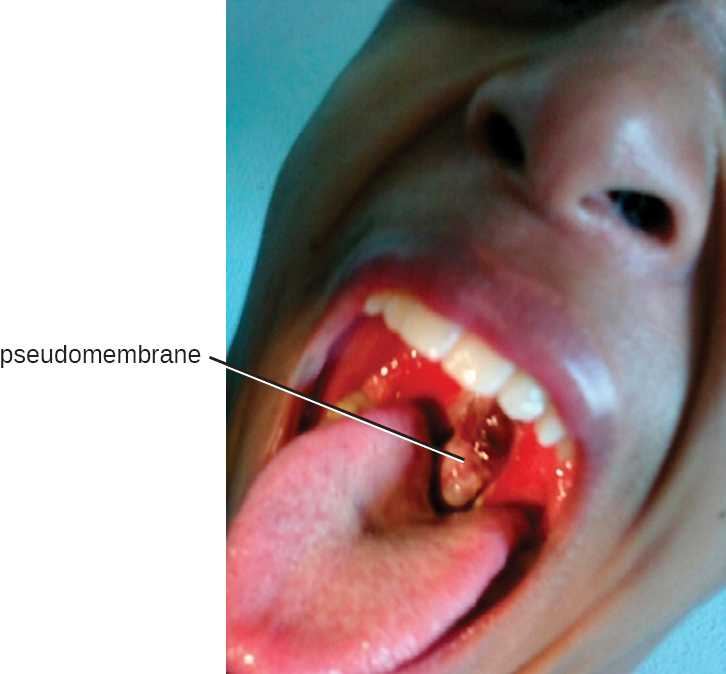
The causative agent of diphtheria , Corynebacterium diphtheriae , is a club-shaped, gram-positive rod that belongs to the phylum Actinobacteria . Diphtheroids are common members of the normal nasopharyngeal microbiota. However, some strains of C. diphtheriae become pathogenic because of the presence of a temperate bacteriophage-encoded protein—the diphtheria toxin . Diphtheria is typically a respiratory infection of the oropharynx but can also cause impetigo-like lesions on the skin. Although the disease can affect people of all ages, it tends to be most severe in those younger than 5 years or older than 40 years. Like strep throat, diphtheria is commonly transmitted in the droplets and aerosols produced by coughing. After colonizing the throat, the bacterium remains in the oral cavity and begins producing the diphtheria toxin. This protein is an A-B toxin that blocks host-cell protein synthesis by inactivating elongation factor (EF)-2 (see Virulence Factors of Bacterial and Viral Pathogens ). The toxin’s action leads to the death of the host cells and an inflammatory response. An accumulation of grayish exudate consisting of dead host cells, pus, red blood cells, fibrin, and infectious bacteria results in the formation of a pseudomembrane . The pseudomembrane can cover mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, tonsils, pharynx, and larynx ( [link] ). This is a classic sign of diphtheria. As the disease progresses, the pseudomembrane can enlarge to obstruct the fauces of the pharynx or trachea and can lead to suffocation and death. Sometimes, intubation , the placement of a breathing tube in the trachea, is required in advanced infections. If the diphtheria toxin spreads throughout the body, it can damage other tissues as well. This can include myocarditis (heart damage) and nerve damage that may impair breathing.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?