| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Pathology associated with HP can be due to both type III (mediated by immune complexes) and type IV (mediated by T H 1 cells and macrophages) hypersensitivities. Repeated exposure to allergens can cause alveolitis due to the formation of immune complexes in the alveolar wall of the lung accompanied by fluid accumulation, and the formation of granuloma s and other lesions in the lung as a result of T H 1-mediated macrophage activation. Alveolitis with fluid and granuloma formation results in poor oxygen perfusion in the alveoli, which, in turn, can cause symptoms such as coughing, dyspnea, chills, fever, sweating, myalgias, headache, and nausea. Symptoms may occur as quickly as 2 hours after exposure and can persist for weeks if left untreated.

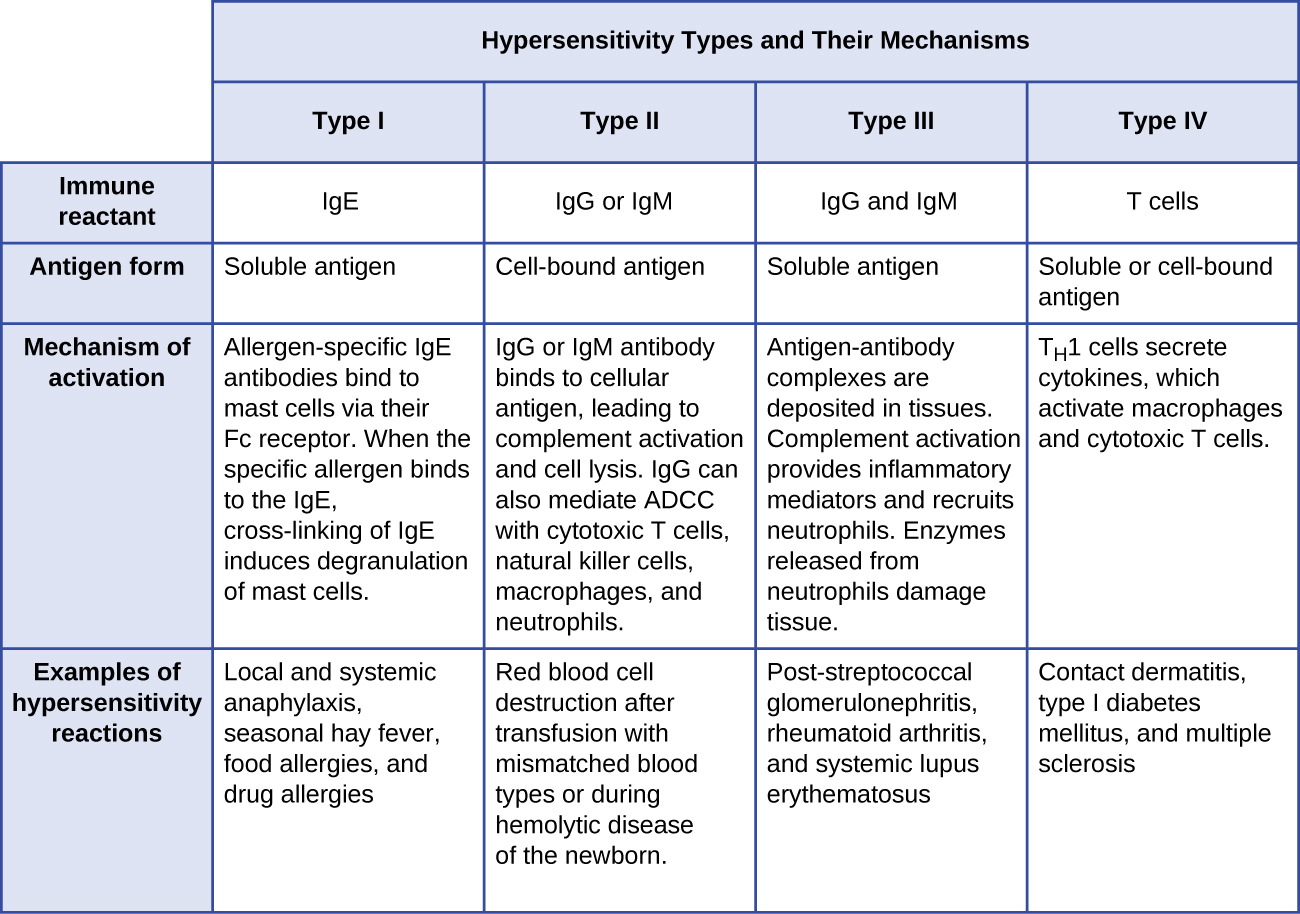
[link] summarizes the mechanisms and effects of each type of hypersensitivity discussed in this section.
Diagnosis of type I hypersensitivities is a complex process requiring several diagnostic tests in addition to a well-documented patient history. Serum IgE levels can be measured, but elevated IgE alone does not confirm allergic disease. As part of the process to identify the antigens responsible for a type I reaction allergy, testing through a prick puncture skin test (PPST) or an intradermal test can be performed. PPST is carried out with the introduction of allergens in a series of superficial skin pricks on the patient’s back or arms ( [link] ). PPSTs are considered to be the most convenient and least expensive way to diagnose allergies, according to the US Joint Council of Allergy and the European Academy of Allergy and Immunology. The second type of testing, the intradermal test, requires injection into the dermis with a small needle. This needle, also known as a tuberculin needle, is attached to a syringe containing a small amount of allergen. Both the PPST and the intradermal tests are observed for 15–20 minutes for a wheal-flare reaction to the allergens. Measurement of any wheal (a raised, itchy bump) and flare (redness) within minutes indicates a type I hypersensitivity, and the larger the wheal-flare reaction, the greater the patient’s sensitivity to the allergen.
Type III hypersensitivities can often be misdiagnosed because of their nonspecific inflammatory nature. The symptoms are easily visible, but they may be associated with any of a number of other diseases. A strong, comprehensive patient history is crucial to proper and accurate diagnosis. Tests used to establish the diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis (resulting from type III hypersensitivity) include bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), pulmonary function tests, and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?