| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
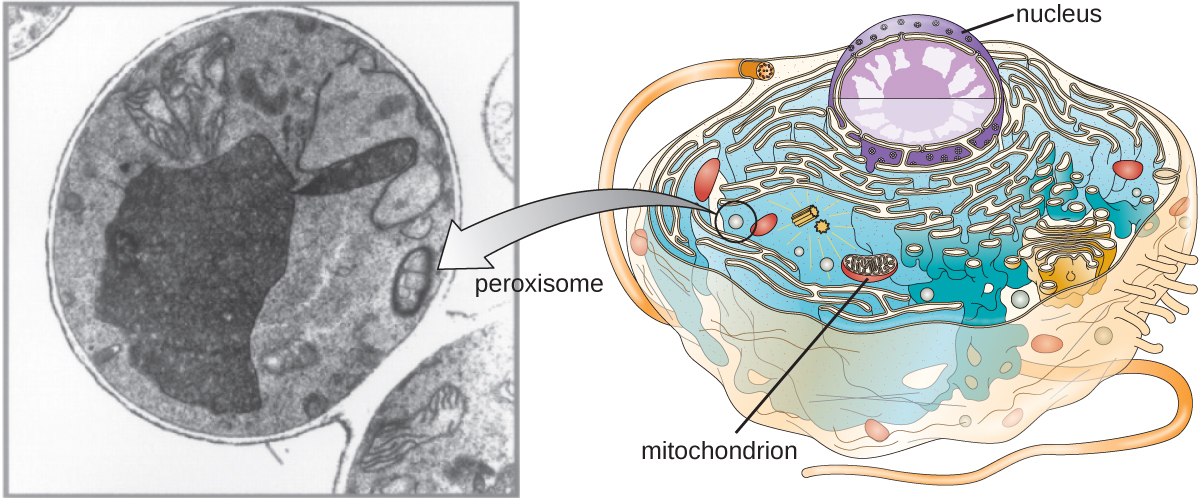
Christian de Duve is also credited with the discovery of peroxisomes , membrane-bound organelles that are not part of the endomembrane system ( [link] ). Peroxisomes form independently in the cytoplasm from the synthesis of peroxin proteins by free ribosomes and the incorporation of these peroxin proteins into existing peroxisomes. Growing peroxisomes then divide by a process similar to binary fission.
Peroxisomes were first named for their ability to produce hydrogen peroxide, a highly reactive molecule that helps to break down molecules such as uric acid, amino acids, and fatty acids. Peroxisomes also possess the enzyme catalase, which can degrade hydrogen peroxide. Along with the SER, peroxisomes also play a role in lipid biosynthesis. Like lysosomes, the compartmentalization of these degradative molecules within an organelle helps protect the cytoplasmic contents from unwanted damage.
The peroxisomes of certain organisms are specialized to meet their particular functional needs. For example, glyoxysomes are modified peroxisomes of yeasts and plant cells that perform several metabolic functions, including the production of sugar molecules. Similarly, glycosomes are modified peroxisomes made by certain trypanosomes, the pathogenic protozoans that cause Chagas disease and African sleeping sickness .
Eukaryotic cells have an internal cytoskeleton made of microfilaments , intermediate filaments , and microtubules . This matrix of fibers and tubes provides structural support as well as a network over which materials can be transported within the cell and on which organelles can be anchored ( [link] ). For example, the process of exocytosis involves the movement of a vesicle via the cytoskeletal network to the plasma membrane, where it can release its contents.
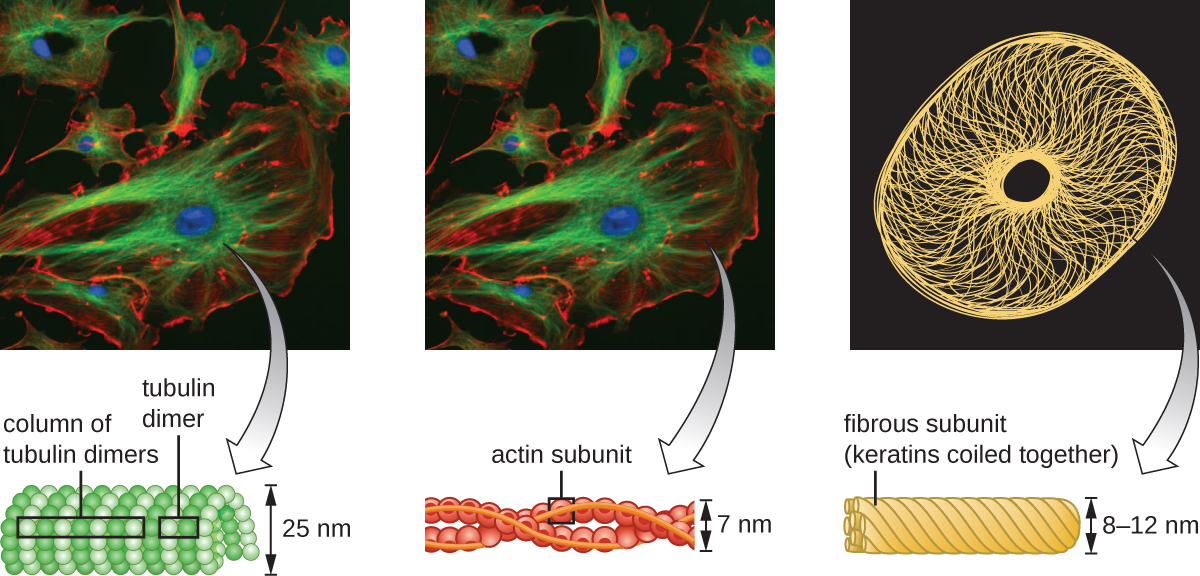
Microfilaments are composed of two intertwined strands of actin, each composed of actin monomers forming filamentous cables 6 nm in diameter Fuchs E, Cleveland DW. “A Structural Scaffolding of Intermediate Filaments in Health and Disease.” Science 279 no. 5350 (1998):514–519. ( [link] ). The actin filaments work together with motor proteins, like myosin, to effect muscle contraction in animals or the amoeboid movement of some eukaryotic microbes. In ameboid organisms, actin can be found in two forms: a stiffer, polymerized, gel form and a more fluid, unpolymerized soluble form. Actin in the gel form creates stability in the ectoplasm, the gel-like area of cytoplasm just inside the plasma membrane of ameboid protozoans.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?