| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Another protozoan intestinal illness is cryptosporidiosis , which is usually caused by Cryptosporidium parvum or C. hominis . ( [link] ) These pathogens are commonly found in animals and can be spread in feces from mice, birds, and farm animals. Contaminated water and food are most commonly responsible for transmission. The protozoan can also be transmitted through human contact with infected animals or their feces.
In the United States, outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis generally occur through contamination of the public water supply or contaminated water at water parks, swimming pools, and day-care centers. The risk is greatest in areas with poor sanitation, making the disease more common in developing countries.
Signs and symptoms include watery diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, cramps, fever, dehydration, and weight loss. The illness is generally self-limiting within a month. However, immunocompromised patients, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are at particular risk of severe illness or death.
Diagnosis involves direct examination of stool samples, often over multiple days. As with giardiasis, a stool O&P exam may be helpful. Acid fast staining is often used. Enzyme immunoassays and molecular analysis (PCR) are available.
The first line of treatment is typically oral rehydration therapy. Medications are sometimes used to treat the diarrhea. The broad-range anti-parasitic drug nitazoxanide can be used to treat cryptosporidiosis. Other anti-parasitic drugs that can be used include azithromycin and paromomycin .
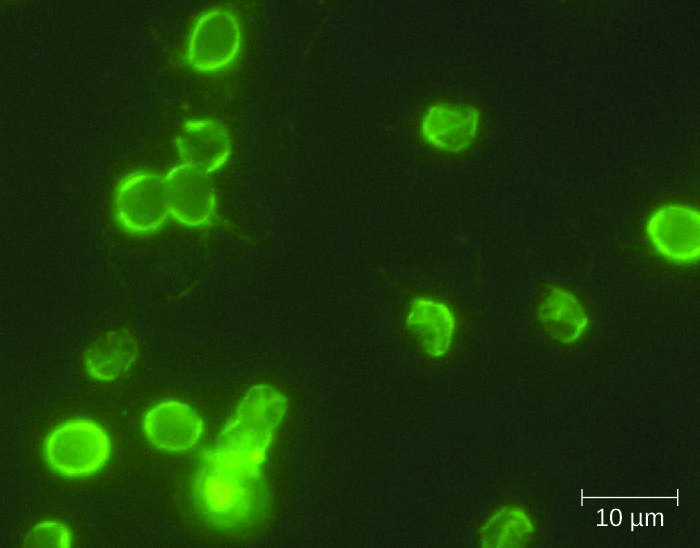
The protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebiasis , which is known as amoebic dysentery in severe cases. E. histolytica is generally transmitted through water or food that has fecal contamination. The disease is most widespread in the developing world and is one of the leading causes of mortality from parasitic disease worldwide. Disease can be caused by as few as 10 cysts being transmitted.
Signs and symptoms range from nonexistent to mild diarrhea to severe amoebic dysentery. Severe infection causes the abdomen to become distended and may be associated with fever. The parasite may live in the colon without causing signs or symptoms or may invade the mucosa to cause colitis. In some cases, the disease spreads to the spleen, brain, genitourinary tract, or lungs. In particular, it may spread to the liver and cause an abscess. When a liver abscess develops, fever, nausea, liver tenderness, weight loss, and pain in the right abdominal quadrant may occur. Chronic infection may occur and is associated with intermittent diarrhea, mucus, pain, flatulence, and weight loss.
Direct examination of fecal specimens may be used for diagnosis. As with cryptosporidiosis, samples are often examined on multiple days. A stool O&P exam of fecal or biopsy specimens may be helpful. Immunoassay, serology, biopsy, molecular, and antibody detection tests are available. Enzyme immunoassay may not distinguish current from past illness. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to detect any liver abscesses. The first line of treatment is metronidazole or tinidazole , followed by diloxanide furoate , iodoquinol , or paromomycin to eliminate the cysts that remain.
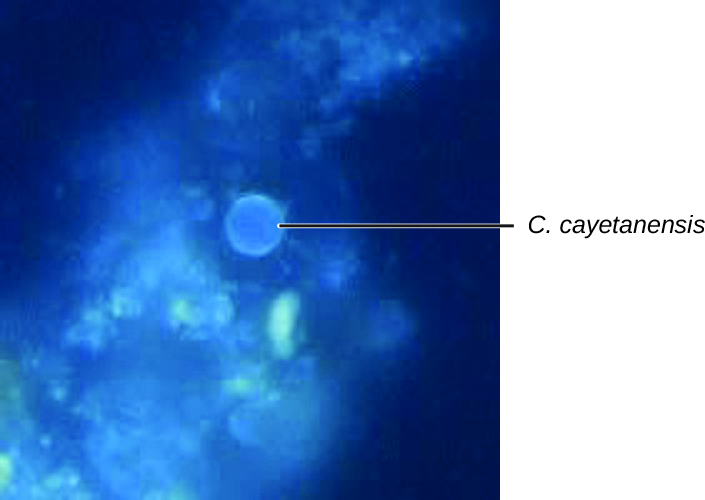
The intestinal disease cyclosporiasis is caused by the protozoan Cyclospora cayetanensis . It is endemic to tropical and subtropical regions and therefore uncommon in the United States, although there have been outbreaks associated with contaminated produce imported from regions where the protozoan is more common.
This protist is transmitted through contaminated food and water and reaches the lining of the small intestine, where it causes infection. Signs and symptoms begin within seven to ten days after ingestion. Based on limited data, it appears to be seasonal in ways that differ regionally and that are poorly understood. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Cyclosporiasis FAQs for Health Professionals.” Updated June 13, 2014. http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/cyclosporiasis/health_professionals/hp-faqs.html.
Some individuals do not develop signs or symptoms. Those who do may exhibit explosive and watery diarrhea, fever, nausea, vomiting, cramps, loss of appetite, fatigue, and bloating. These symptoms may last for months without treatment. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the recommended treatment.
Microscopic examination is used for diagnosis. A stool O&P examination may be helpful. The oocysts have a distinctive blue halo when viewed using ultraviolet fluorescence microscopy ( [link] ).

Protozoan GI infections are generally transmitted through contaminated food or water, triggering diarrhea and vomiting that can lead to dehydration. Rehydration therapy is an important aspect of treatment, but most protozoan GI infections can also be treated with drugs that target protozoans.
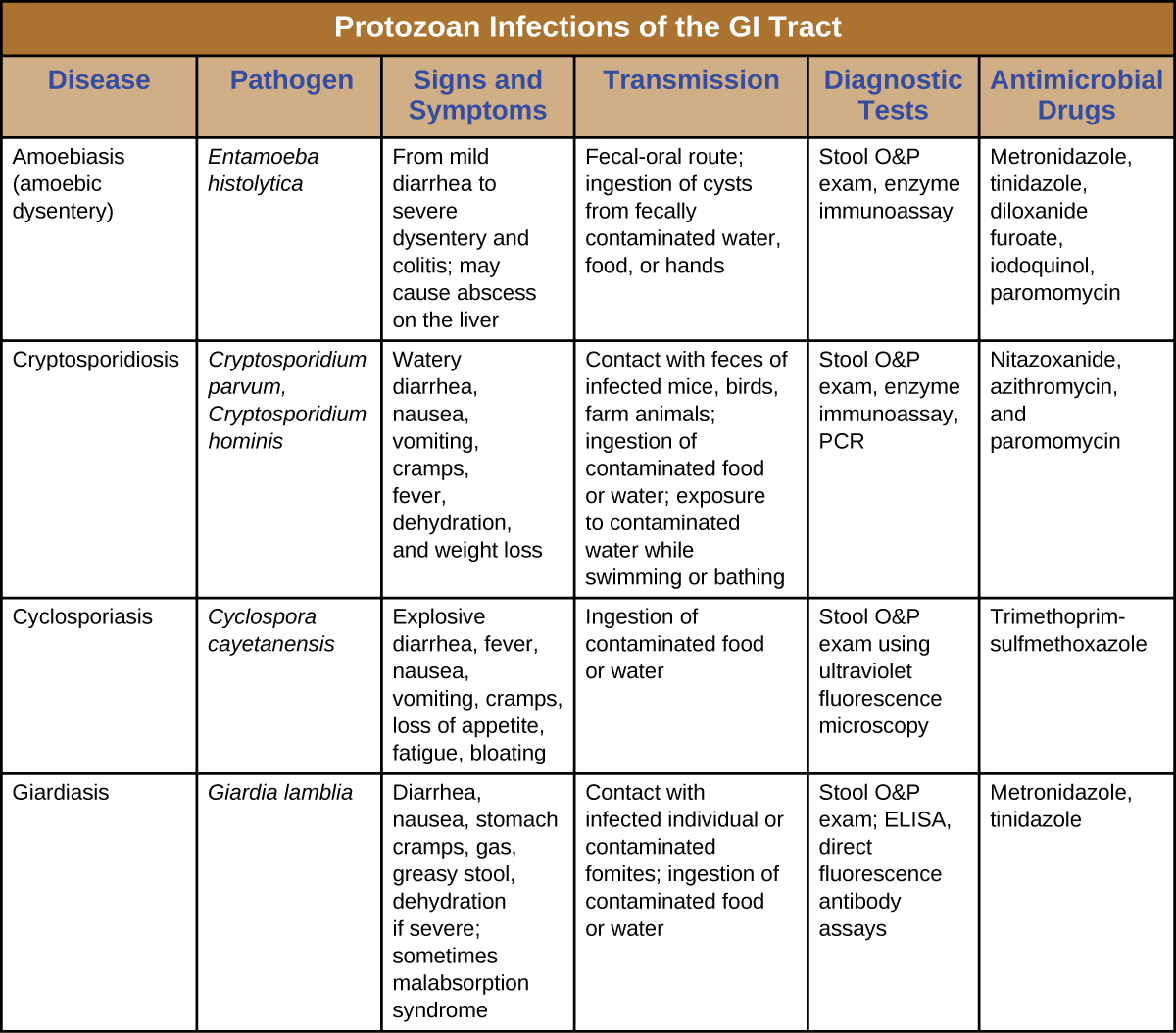
Chronic _________ infections cause the unique sign of disease of greasy stool and are often resistant to treatment.
giardia
What is an O&P exam?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?