| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
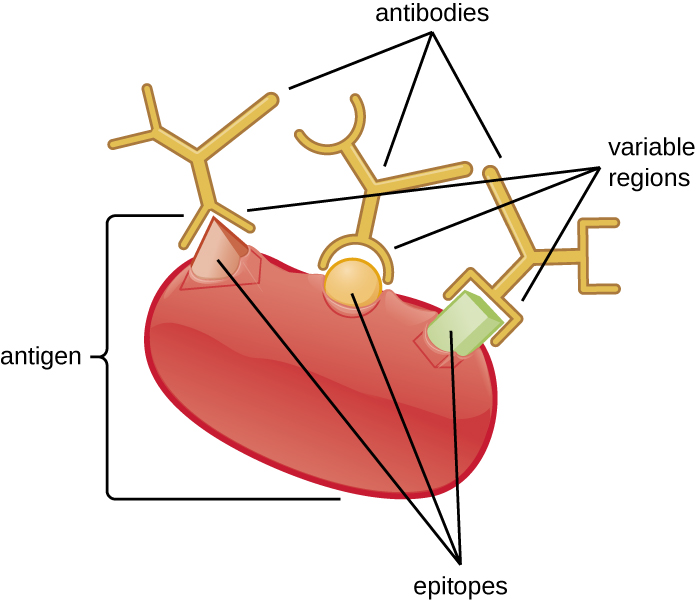
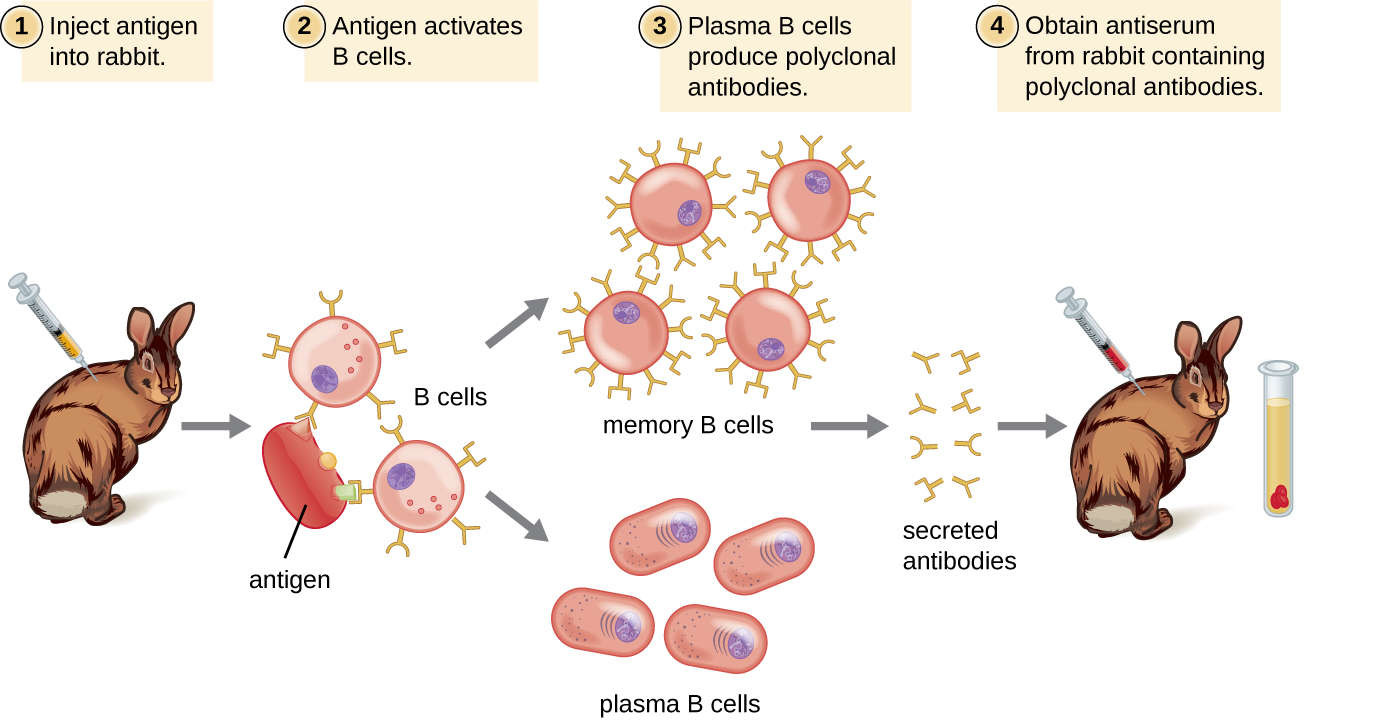
Antibodies used for research and diagnostic purposes are often obtained by injecting a lab animal such as a rabbit or a goat with a specific antigen . Within a few weeks, the animal’s immune system will produce high levels of antibodies specific for the antigen. These antibodies can be harvested in an antiserum , which is whole serum collected from an animal following exposure to an antigen. Because most antigens are complex structures with multiple epitopes, they result in the production of multiple antibodies in the lab animal. This so-called polyclonal antibody response is also typical of the response to infection by the human immune system. Antiserum drawn from an animal will thus contain antibodies from multiple clones of B cells, with each B cell responding to a specific epitope on the antigen ( [link] ).
Lab animals are usually injected at least twice with antigen when being used to produce antiserum. The second injection will activate memory cells that make class IgG antibodies against the antigen. The memory cells also undergo affinity maturation , resulting in a pool of antibodies with higher average affinity. Affinity maturation occurs because of mutations in the immunoglobulin gene variable regions, resulting in B cells with slightly altered antigen-binding sites. On re-exposure to the antigen, those B cells capable of producing antibody with higher affinity antigen-binding sites will be stimulated to proliferate and produce more antibody than their lower-affinity peers. An adjuvant , which is a chemical that provokes a generalized activation of the immune system that stimulates greater antibody production, is often mixed with the antigen prior to injection.
Antiserum obtained from animals will not only contain antibodies against the antigen artificially introduced in the laboratory, but it will also contain antibodies to any other antigens to which the animal has been exposed during its lifetime. For this reason, antisera must first be “purified” to remove other antibodies before using the antibodies for research or diagnostic assays.
Polyclonal antisera are used in many clinical tests that are designed to determine whether a patient is producing antibodies in response to a particular pathogen. While these tests are certainly powerful diagnostic tools, they have their limitations, because they are an indirect means of determining whether a particular pathogen is present. Tests based on a polyclonal response can sometimes lead to a false-positive result—in other words, a test that confirms the presence of an antigen that is, in fact, not present. Antibody-based tests can also result in a false-negative result, which occurs when the test fails to detect an antibody that is, in fact, present.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?