| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When acute inflammation is unable to clear an infectious pathogen, chronic inflammation may occur. This often results in an ongoing (and sometimes futile) lower-level battle between the host organism and the pathogen. The wounded area may heal at a superficial level, but pathogens may still be present in deeper tissues, stimulating ongoing inflammation. Additionally, chronic inflammation may be involved in the progression of degenerative neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, heart disease, and metastatic cancer.
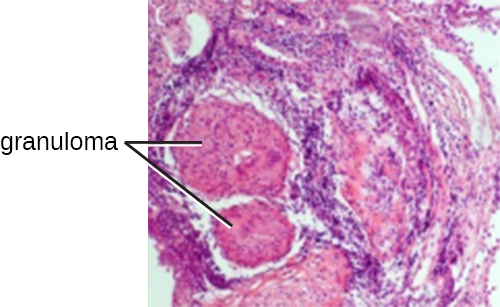
Chronic inflammation may lead to the formation of granuloma s , pockets of infected tissue walled off and surrounded by WBCs. Macrophages and other phagocytes wage an unsuccessful battle to eliminate the pathogens and dead cellular materials within a granuloma. One example of a disease that produces chronic inflammation is tuberculosis , which results in the formation of granulomas in lung tissues. A tubercular granuloma is called a tubercle ( [link] ). Tuberculosis will be covered in more detail in Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract .
Chronic inflammation is not just associated with bacterial infections. Chronic inflammation can be an important cause of tissue damage from viral infections. The extensive scarring observed with hepatitis C infections and liver cirrhosis is the result of chronic inflammation.
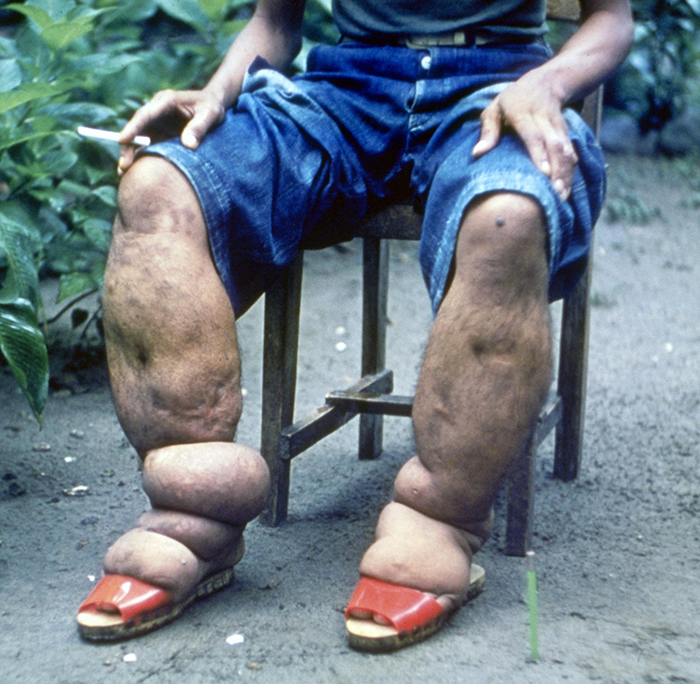
In addition to granulomas, chronic inflammation can also result in long-term edema. A condition known as lymphatic filariasis (also known as elephantiasis ) provides an extreme example. Lymphatic filariasis is caused by microscopic nematodes (parasitic worms) whose larvae are transmitted between human hosts by mosquitoes. Adult worms live in the lymphatic vessels, where their presence stimulates infiltration by lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils, and thrombocytes (a condition known as lymphangitis). Because of the chronic nature of the illness, granulomas, fibrosis, and blocking of the lymphatic system may eventually occur. Over time, these blockages may worsen with repeated infections over decades, leading to skin thickened with edema and fibrosis. Lymph (extracellular tissue fluid) may spill out of the lymphatic areas and back into tissues, causing extreme swelling ( [link] ). Secondary bacterial infections commonly follow. Because it is a disease caused by a parasite, eosinophilia (a dramatic rise in the number of eosinophils in the blood) is characteristic of acute infection. However, this increase in antiparasite granulocytes is not sufficient to clear the infection in many cases.
Lymphatic filariasis affects an estimated 120 million people worldwide, mostly concentrated in Africa and Asia. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Parasites–Lymphatic Filiariasis.” 2016. http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/lymphaticfilariasis/gen_info/faqs.html. Improved sanitation and mosquito control can reduce transmission rates.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?