| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
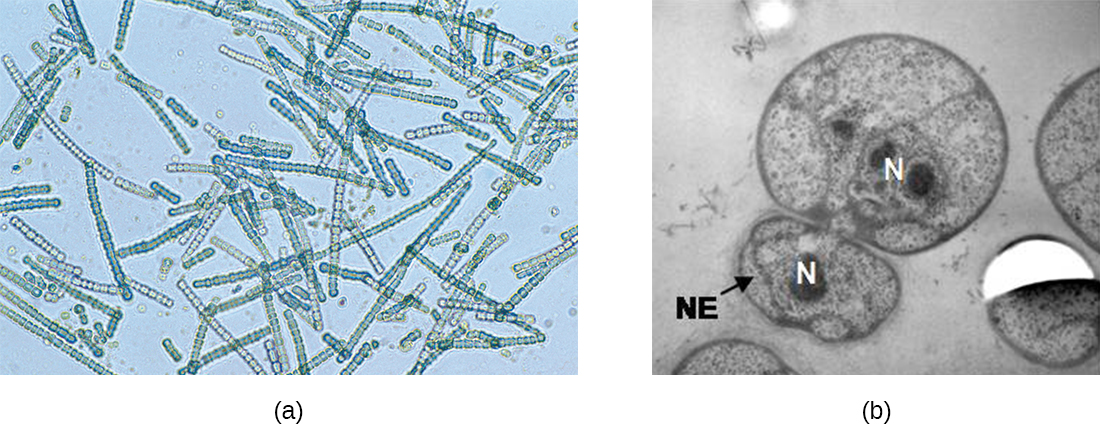
The soil bacteria Actinomyces grow in long filaments divided by septa, similar to the mycelia seen in fungi, resulting in long cells with multiple nucleoids. Environmental signals, probably related to low nutrient availability, lead to the formation of aerial filaments. Within these aerial filaments , elongated cells divide simultaneously. The new cells, which contain a single nucleoid, develop into spores that give rise to new colonies.
In nature, microorganisms grow mainly in biofilms , complex and dynamic ecosystems that form on a variety of environmental surfaces, from industrial conduits and water treatment pipelines to rocks in river beds. Biofilms are not restricted to solid surface substrates, however. Almost any surface in a liquid environment containing some minimal nutrients will eventually develop a biofilm. Microbial mats that float on water, for example, are biofilms that contain large populations of photosynthetic microorganisms. Biofilms found in the human mouth may contain hundreds of bacterial species. Regardless of the environment where they occur, biofilms are not random collections of microorganisms; rather, they are highly structured communities that provide a selective advantage to their constituent microorganisms.
Observations using confocal microscopy have shown that environmental conditions influence the overall structure of biofilms. Filamentous biofilms called streamers form in rapidly flowing water, such as freshwater streams, eddies, and specially designed laboratory flow cells that replicate growth conditions in fast-moving fluids. The streamers are anchored to the substrate by a “head” and the “tail” floats downstream in the current. In still or slow-moving water, biofilms mainly assume a mushroom-like shape. The structure of biofilms may also change with other environmental conditions such as nutrient availability.
Detailed observations of biofilms under confocal laser and scanning electron microscopes reveal clusters of microorganisms embedded in a matrix interspersed with open water channels. The extracellular matrix consists of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) secreted by the organisms in the biofilm. The extracellular matrix represents a large fraction of the biofilm, accounting for 50%–90% of the total dry mass. The properties of the EPS vary according to the resident organisms and environmental conditions.
EPS is a hydrated gel composed primarily of polysaccharides and containing other macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. It plays a key role in maintaining the integrity and function of the biofilm. Channels in the EPS allow movement of nutrients, waste, and gases throughout the biofilm. This keeps the cells hydrated, preventing desiccation. EPS also shelters organisms in the biofilm from predation by other microbes or cells (e.g., protozoans, white blood cells in the human body).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?