| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The presumptive diagnosis of diphtheria is primarily based on the clinical symptoms (i.e., the pseudomembrane) and vaccination history, and is typically confirmed by identifying bacterial cultures obtained from throat swabs. The diphtheria toxin itself can be directly detected in vitro using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based, direct detection systems for the diphtheria tox gene, and immunological techniques like radial immunodiffusion or Elek’s immunodiffusion test.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics like penicillin and erythromycin tend to effectively control C. diphtheriae infections. Regrettably, they have no effect against preformed toxins. If toxin production has already occurred in the patient, antitoxins (preformed antibodies against the toxin) are administered. Although this is effective in neutralizing the toxin, the antitoxins may lead to serum sickness because they are produced in horses (see Hypersensitivities ).
Widespread vaccination efforts have reduced the occurrence of diphtheria worldwide. There are currently four combination toxoid vaccines available that provide protection against diphtheria and other diseases: DTaP, Tdap, DT, and Td. In all cases, the letters “d,” “t,” and “p” stand for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis, respectively; the “a” stands for acellular. If capitalized, the letters indicate a full-strength dose; lowercase letters indicate reduced dosages. According to current recommendations, children should receive five doses of the DTaP vaccine in their youth and a Td booster every 10 years. Children with adverse reactions to the pertussis vaccine may be given the DT vaccine in place of the DTaP.
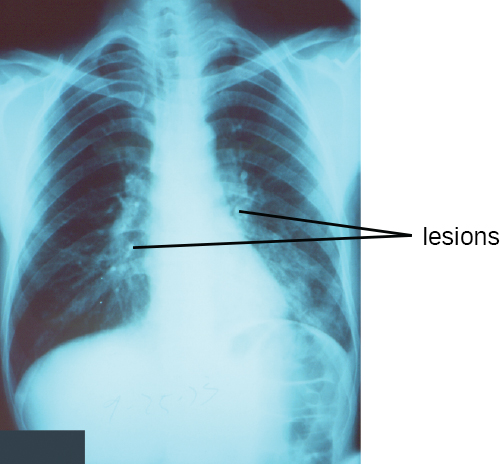
Pneumonia is a general term for infections of the lungs that lead to inflammation and accumulation of fluids and white blood cells in the alveoli. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other organisms, although the vast majority of pneumonias are bacterial in origin. Bacterial pneumonia is a prevalent, potentially serious infection; it caused more 50,000 deaths in the United States in 2014. KD Kochanek et al. “Deaths: Final Data for 2014.” National Vital Statistics Reports 65 no 4 (2016). As the alveoli fill with fluids and white blood cells (consolidation), air exchange becomes impaired and patients experience respiratory distress ( [link] ). In addition, pneumonia can lead to pleurisy , an infection of the pleural membrane surrounding the lungs, which can make breathing very painful. Although many different bacteria can cause pneumonia under the right circumstances, three bacterial species cause most clinical cases: Streptococcus pneumoniae , H . influenzae , and Mycoplasma pneumoniae . In addition to these, we will also examine some of the less common causes of pneumonia.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?