| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
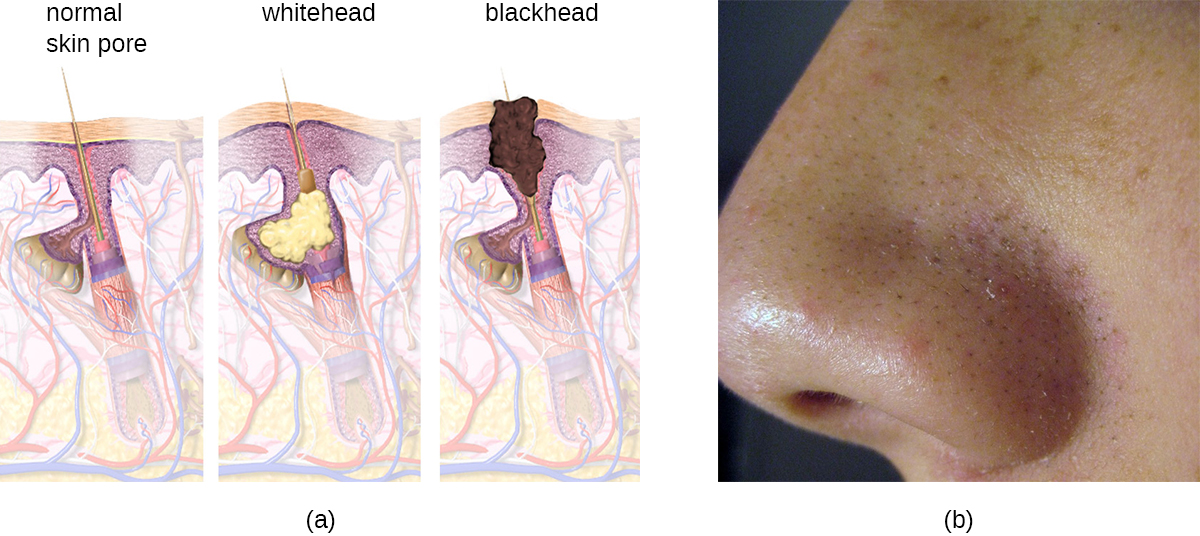
Often comedones lead to infection by Propionibacterium acnes , a gram-positive, non-spore-forming, aerotolerant anaerobic bacillus found on skin that consumes components of sebum. P. acnes secretes enzymes that damage the hair follicle, causing inflammatory lesions that may include papules , pustules , nodules , or pseudocysts, depending on their size and severity.
Treatment of acne depends on the severity of the case. There are multiple ways to grade acne severity, but three levels are usually considered based on the number of comedones, the number of inflammatory lesions, and the types of lesions. Mild acne is treated with topical agents that may include salicylic acid (which helps to remove old skin cells) or retinoids (which have multiple mechanisms, including the reduction of inflammation). Moderate acne may be treated with antibiotics ( erythromycin , clindamycin ), acne creams (e.g., benzoyl peroxide ), and hormones. Severe acne may require treatment using strong medications such as isotretinoin (a retinoid that reduces oil buildup, among other effects, but that also has serious side effects such as photosensitivity). Other treatments, such as phototherapy and laser therapy to kill bacteria and possibly reduce oil production, are also sometimes used.
Sam uses the topical antibiotic over the weekend to treat his wound, but he does not see any improvement. On Monday, the doctor calls to inform him that the results from his laboratory tests are in. The tests show evidence of both Staphylococcus and Streptococcus in his wound. The bacterial species were confirmed using several tests. A passive agglutination test confirmed the presence of S. aureus . In this type of test, latex beads with antibodies cause agglutination when S. aureus is present. Streptococcus pyogenes was confirmed in the wound based on bacitracin (0.04 units) susceptibility as well as latex agglutination tests specific for S. pyogenes .
Because many strains of S. aureus are resistant to antibiotics, the doctor had also requested an antimicrobial susceptibility test (AST) at the same time the specimen was submitted for identification. The results of the AST indicated no drug resistance for the Streptococcus spp.; the Staphylococcus spp. showed resistance to several common antibiotics, but were susceptible to cefoxitin and oxacillin. Once Sam began to use these new antibiotics, the infection resolved within a week and the lesion healed.
Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
The zoonotic disease anthrax is caused by Bacillus anthracis , a gram-positive, endospore-forming, facultative anaerobe. Anthrax mainly affects animals such as sheep, goats, cattle, and deer, but can be found in humans as well. Sometimes called wool sorter’s disease , it is often transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals or animal products, such as wool or hides. However, exposure to B. anthracis can occur by other means, as the endospores are widespread in soils and can survive for long periods of time, sometimes for hundreds of years.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?