| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
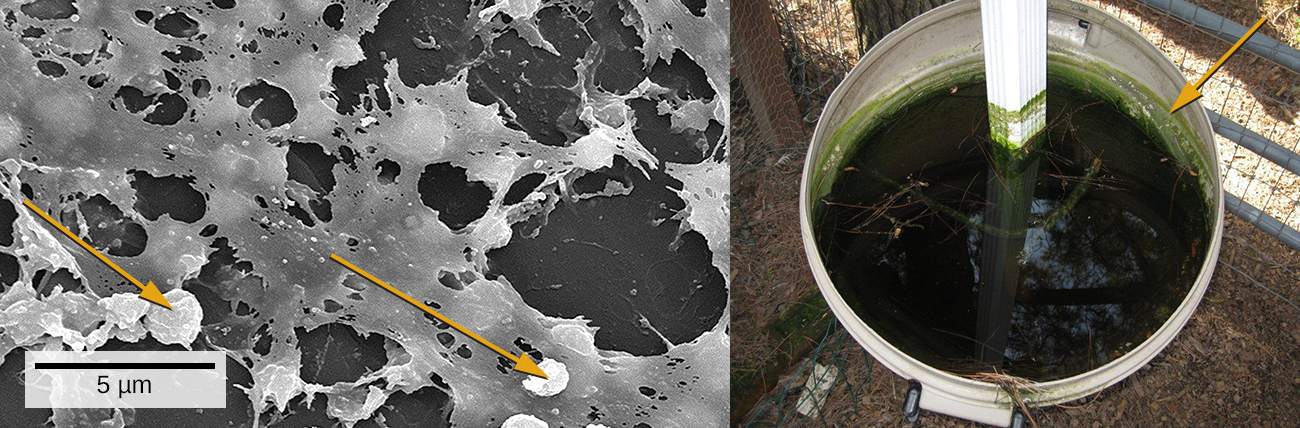
We are all familiar with the slimy layer on a pond surface or that makes rocks slippery. These are examples of biofilms—microorganisms embedded in thin layers of matrix material ( [link] ). Biofilms were long considered random assemblages of cells and had little attention from researchers. Recently, progress in visualization and biochemical methods has revealed that biofilms are an organized ecosystem within which many cells, usually of different species of bacteria, fungi, and algae, interact through cell signaling and coordinated responses. The biofilm provides a protected environment in harsh conditions and aids colonization by microorganisms. Biofilms also have clinical importance. They form on medical devices, resist routine cleaning and sterilization, and cause health-acquired infections. Within the body, biofilms form on the teeth as plaque, in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis, and on the cardiac tissue of patients with endocarditis. The slime layer helps protect the cells from host immune defenses and antibiotic treatments.
Studying biofilms requires new approaches. Because of the cells’ adhesion properties, many of the methods for culturing and counting cells that are explored in this chapter are not easily applied to biofilms. This is the beginning of a new era of challenges and rewarding insight into the ways that microorganisms grow and thrive in nature.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?