| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Hannah is a 15-month-old girl from Washington state. She is spending the summer in Gambia, where her parents are working for a nongovernmental organization. About 3 weeks after her arrival in Gambia, Hannah’s appetite began to diminish and her parents noticed that she seemed unusually sluggish, fatigued, and confused. She also seemed very irritable when she was outdoors, especially during the day. When she began vomiting, her parents figured she had caught a 24-hour virus, but when her symptoms persisted, they took her to a clinic. The local physician noticed that Hannah’s reflexes seemed abnormally slow, and when he examined her eyes with a light, she seemed unusually light sensitive. She also seemed to be experiencing a stiff neck.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box.
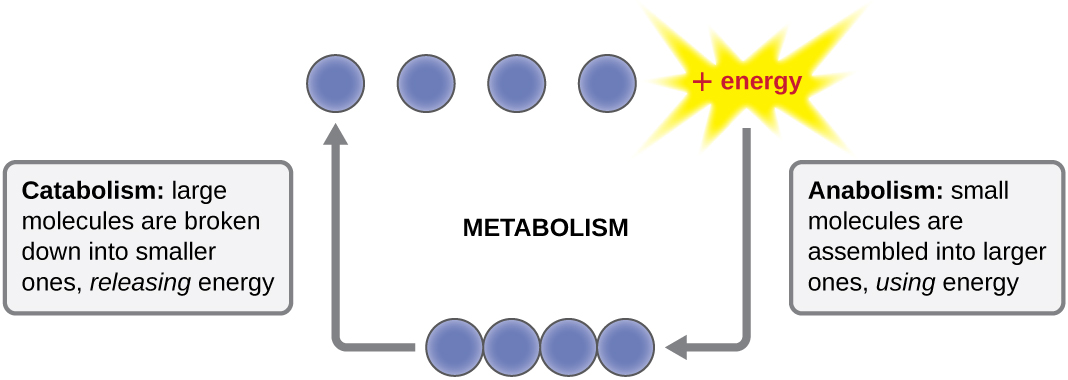
The term used to describe all of the chemical reactions inside a cell is metabolism ( [link] ). Cellular processes such as the building or breaking down of complex molecules occur through series of stepwise, interconnected chemical reactions called metabolic pathway s. Reactions that are spontaneous and release energy are exergonic reaction s, whereas endergonic reaction s require energy to proceed. The term anabolism refers to those endergonic metabolic pathways involved in biosynthesis , converting simple molecular building blocks into more complex molecules, and fueled by the use of cellular energy. Conversely, the term catabolism refers to exergonic pathways that break down complex molecules into simpler ones. Molecular energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules is released in catabolic pathways and harvested in such a way that it can be used to produce high-energy molecules, which are used to drive anabolic pathways. Thus, in terms of energy and molecules, cells are continually balancing catabolism with anabolism.
Organisms can be identified according to the source of carbon they use for metabolism as well as their energy source. The prefixes auto- (“self”) and hetero- (“other”) refer to the origins of the carbon sources various organisms can use. Organisms that convert inorganic carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into organic carbon compounds are autotroph s . Plants and cyanobacteria are well-known examples of autotrophs. Conversely, heterotroph s rely on more complex organic carbon compounds as nutrients; these are provided to them initially by autotrophs. Many organisms, ranging from humans to many prokaryotes, including the well-studied Escherichia coli , are heterotrophic.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?