| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Describe the chemical composition of lipids
Although they are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, lipid molecules may also contain oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorous. Lipids serve numerous and diverse purposes in the structure and functions of organisms. They can be a source of nutrients, a storage form for carbon, energy-storage molecules, or structural components of membranes and hormones. Lipids comprise a broad class of many chemically distinct compounds, the most common of which are discussed in this section.
The fatty acid s are lipids that contain long-chain hydrocarbons terminated with a carboxylic acid functional group. Because the long hydrocarbon chain , fatty acids are hydrophobic (“water fearing”) or nonpolar . Fatty acids with hydrocarbon chains that contain only single bonds are called saturated fatty acid s because they have the greatest number of hydrogen atoms possible and are, therefore, “saturated” with hydrogen. Fatty acids with hydrocarbon chains containing at least one double bond are called unsaturated fatty acid s because they have fewer hydrogen atoms. Saturated fatty acids have a straight, flexible carbon backbone, whereas unsaturated fatty acids have “kinks” in their carbon skeleton because each double bond causes a rigid bend of the carbon skeleton. These differences in saturated versus unsaturated fatty acid structure result in different properties for the corresponding lipids in which the fatty acids are incorporated. For example, lipids containing saturated fatty acids are solids at room temperature, whereas lipids containing unsaturated fatty acids are liquids.
A triacylglycerol , or triglyceride , is formed when three fatty acids are chemically linked to a glycerol molecule ( [link] ). Triglycerides are the primary components of adipose tissue (body fat), and are major constituents of sebum (skin oils). They play an important metabolic role, serving as efficient energy-storage molecules that can provide more than double the caloric content of both carbohydrates and proteins .
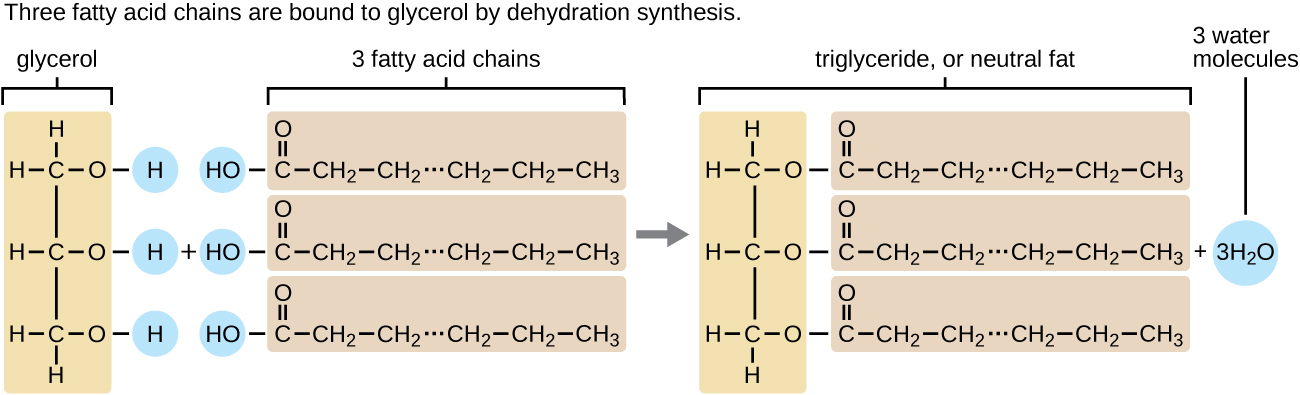
Triglycerides are classified as simple lipids because they are formed from just two types of compounds: glycerol and fatty acids . In contrast, complex lipids contain at least one additional component, for example, a phosphate group ( phospholipid s ) or a carbohydrate moiety ( glycolipid s ). [link] depicts a typical phospholipid composed of two fatty acids linked to glycerol (a diglyceride ). The two fatty acid carbon chains may be both saturated, both unsaturated, or one of each. Instead of another fatty acid molecule (as for triglycerides), the third binding position on the glycerol molecule is occupied by a modified phosphate group.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?