| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
No one has to worry about getting sick from a lichen infection, but lichens are interesting from a microbiological perspective and they are an important component of most terrestrial ecosystems. Lichens provide opportunities for study of close relationships between unrelated microorganisms. Lichens contribute to soil production by breaking down rock, and they are early colonizers in soilless environments such as lava flows. The cyanobacteria in some lichens can fix nitrogen and act as a nitrogen source in some environments. Lichens are also important soil stabilizers in some desert environments and they are an important winter food source for caribou and reindeer. Finally, lichens produce compounds that have antibacterial effects, and further research may discover compounds that are medically useful to humans.
A lichen is a combination of two organisms, a green alga or cyanobacterium and an ascomycete fungus, living in a symbiotic relationship. Whereas algae normally grow only in aquatic or extremely moist environments, lichens can potentially be found on almost any surface (especially rocks) or as epiphytes (meaning that they grow on other plants).
In some ways, the symbiotic relationship between lichens and algae seems like a mutualism (a relationship in which both organisms benefit). The fungus can obtain photosynthates from the algae or cyanobacterium and the algae or cyanobacterium can grow in a drier environment than it could otherwise tolerate. However, most scientists consider this symbiotic relationship to be a controlled parasitism (a relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is harmed) because the photosynthetic organism grows less well than it would without the fungus. It is important to note that such symbiotic interactions fall along a continuum between conflict and cooperation.
Lichens are slow growing and can live for centuries. They have been used in foods and to extract chemicals as dyes or antimicrobial substances. Some are very sensitive to pollution and have been used as environmental indicators.
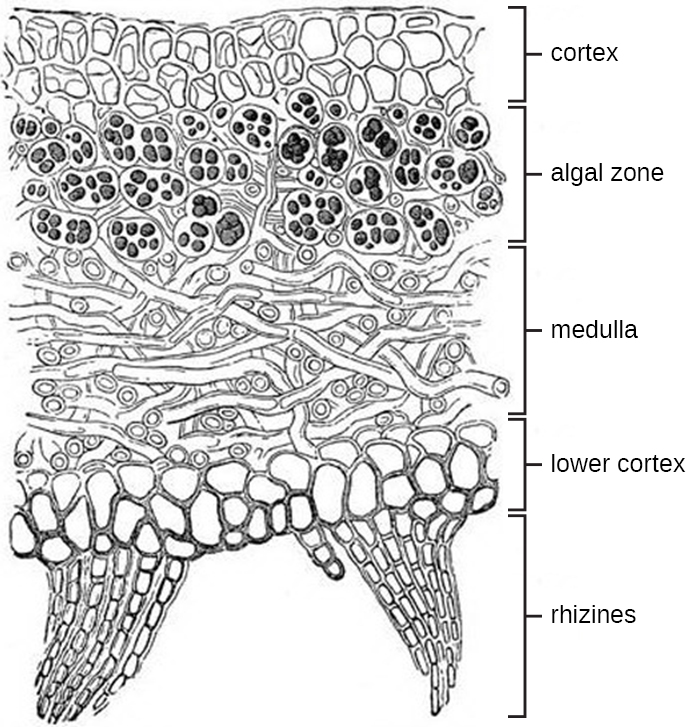
Lichens have a body called a thallus, an outer, tightly packed fungal layer called a cortex , and an inner, loosely packed fungal layer called a medulla ( [link] ). Lichens use hyphal bundles called rhizines to attach to the substrate.
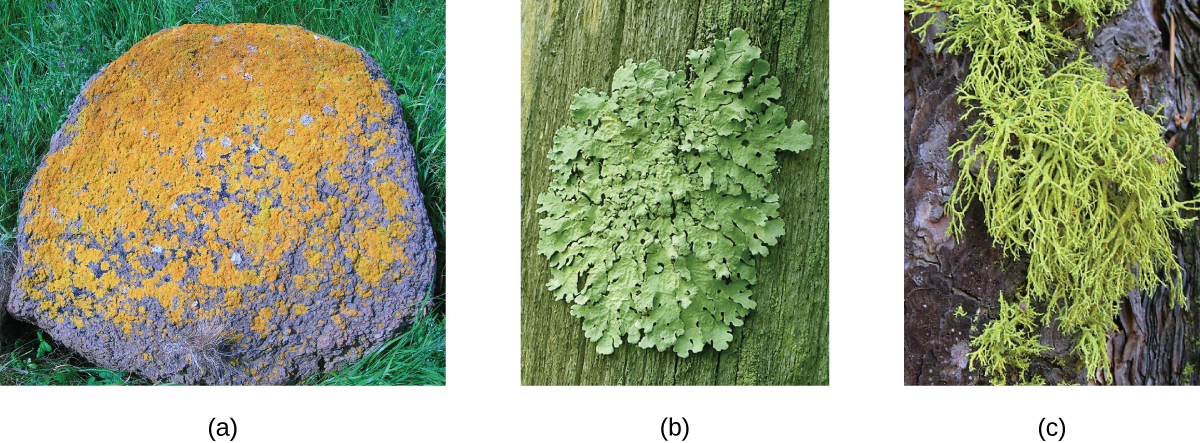
Lichens are classified as fungi and the fungal partners belong to the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota. Lichens can also be grouped into types based on their morphology. There are three major types of lichens, although other types exist as well. Lichens that are tightly attached to the substrate, giving them a crusty appearance, are called crustose lichens . Those that have leaf-like lobes are foliose lichens ; they may only be attached at one point in the growth form, and they also have a second cortex below the medulla. Finally, fruticose lichens have rounded structures and an overall branched appearance. [link] shows an example of each of the forms of lichens.

Sarah’s mother asks the doctor what she should do if the cream prescribed for Sarah’s ringworm does not work. The doctor explains that ringworm is a general term for a condition caused by multiple species. The first step is to take a scraping for examination under the microscope, which the doctor has already done. He explains that he has identified the infection as a fungus, and that the antifungal cream works against the most common fungi associated with ringworm. However, the cream may not work against some species of fungus. If the cream is not working after a couple of weeks, Sarah should come in for another visit, at which time the doctor will take steps to identify the species of the fungus.
Positive identification of dermatophytes requires culturing. For this purpose, Sabouraud’s agar may be used. In the case of Sarah’s infection, which cleared up within 2 weeks of treatment, the culture would have a granular texture and would appear pale pink on top and red underneath. These features suggest that the fungus is Trichophyton rubrum , a common cause of ringworm.
Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
What are three ways that lichens are environmentally valuable?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?