| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
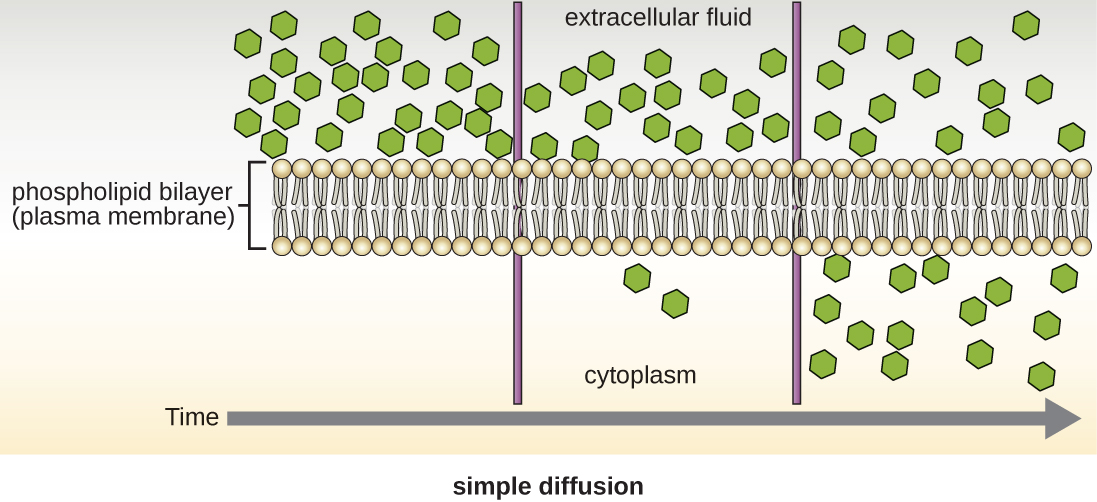
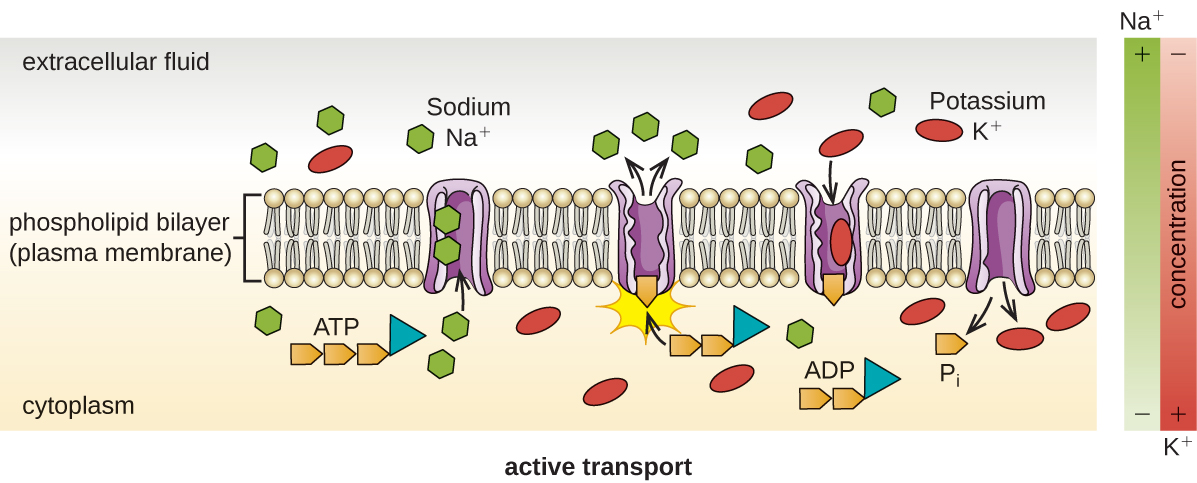
Active transport occurs when cells move molecules across their membrane against concentration gradients ( [link] ). A major difference between passive and active transport is that active transport requires adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or other forms of energy to move molecules “uphill.” Therefore, active transport structures are often called “pumps.”

Group translocation also transports substances into bacterial cells. In this case, as a molecule moves into a cell against its concentration gradient, it is chemically modified so that it does not require transport against an unfavorable concentration gradient. A common example of this is the bacterial phosphotransferase system, a series of carriers that phosphorylates (i.e., adds phosphate ions to) glucose or other sugars upon entry into cells. Since the phosphorylation of sugars is required during the early stages of sugar metabolism, the phosphotransferase system is considered to be an energy neutral system.
Some prokaryotic cells, namely cyanobacteria and photosynthetic bacteria , have membrane structures that enable them to perform photosynthesis. These structures consist of an infolding of the plasma membrane that encloses photosynthetic pigments such as green chlorophylls and bacteriochlorophylls . In cyanobacteria, these membrane structures are called thylakoids; in photosynthetic bacteria, they are called chromatophores, lamellae, or chlorosomes.
The primary function of the cell wall is to protect the cell from harsh conditions in the outside environment. When present, there are notable similarities and differences among the cell walls of archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes.
The major component of bacterial cell walls is called peptidoglycan (or murein ); it is only found in bacteria. Structurally, peptidoglycan resembles a layer of meshwork or fabric ( [link] ). Each layer is composed of long chains of alternating molecules of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). The structure of the long chains has significant two-dimensional tensile strength due to the formation of peptide bridges that connect NAG and NAM within each peptidoglycan layer. In gram-negative bacteria, tetrapeptide chains extending from each NAM unit are directly cross-linked, whereas in gram-positive bacteria, these tetrapeptide chains are linked by pentaglycine cross-bridges. Peptidoglycan subunits are made inside of the bacterial cell and then exported and assembled in layers, giving the cell its shape.
Since peptidoglycan is unique to bacteria, many antibiotic drugs are designed to interfere with peptidoglycan synthesis, weakening the cell wall and making bacterial cells more susceptible to the effects of osmotic pressure (see Mechanisms of Antibacterial Drugs ). In addition, certain cells of the human immune system are able “recognize” bacterial pathogens by detecting peptidoglycan on the surface of a bacterial cell; these cells then engulf and destroy the bacterial cell, using enzymes such as lysozyme, which breaks down and digests the peptidoglycan in their cell walls (see Pathogen Recognition and Phagocytosis ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?