| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Fungal infections of the nervous system, called neuromycoses , are rare in healthy individuals. However, neuromycoses can be devastating in immunocompromised or elderly patients. Several eukaryotic parasites are also capable of infecting the nervous system of human hosts. Although relatively uncommon, these infections can also be life-threatening in immunocompromised individuals. In this section, we will first discuss neuromycoses, followed by parasitic infections of the nervous system.
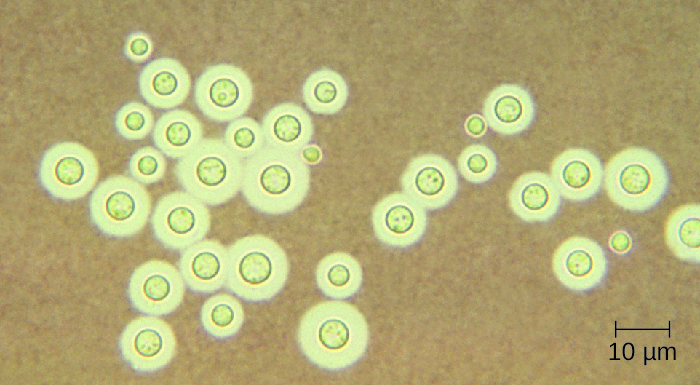
Cryptococcus neoformans is a fungal pathogen that can cause meningitis. This yeast is commonly found in soils and is particularly associated with pigeon droppings. It has a thick capsule that serves as an important virulence factor , inhibiting clearance by phagocytosis. Most C. neoformans cases result in subclinical respiratory infections that, in healthy individuals, generally resolve spontaneously with no long-term consequences (see Respiratory Mycoses ). In immunocompromised patients or those with other underlying illnesses, the infection can progress to cause meningitis and granuloma formation in brain tissues. Cryptococcus antigens can also serve to inhibit cell-mediated immunity and delayed-type hypersensitivity.
Cryptococcus can be easily cultured in the laboratory and identified based on its extensive capsule ( [link] ). C. neoformans is frequently cultured from urine samples of patients with disseminated infections.
Prolonged treatment with antifungal drugs is required to treat cryptococcal infections. Combined therapy is required with amphotericin B plus flucytosine for at least 10 weeks. Many antifungal drugs have difficulty crossing the blood-brain barrier and have strong side effects that necessitate low doses; these factors contribute to the lengthy time of treatment. Patients with AIDS are particularly susceptible to Cryptococcus infections because of their compromised immune state. AIDS patients with cryptococcosis can also be treated with antifungal drugs, but they often have relapses; lifelong doses of fluconazole may be necessary to prevent reinfection.
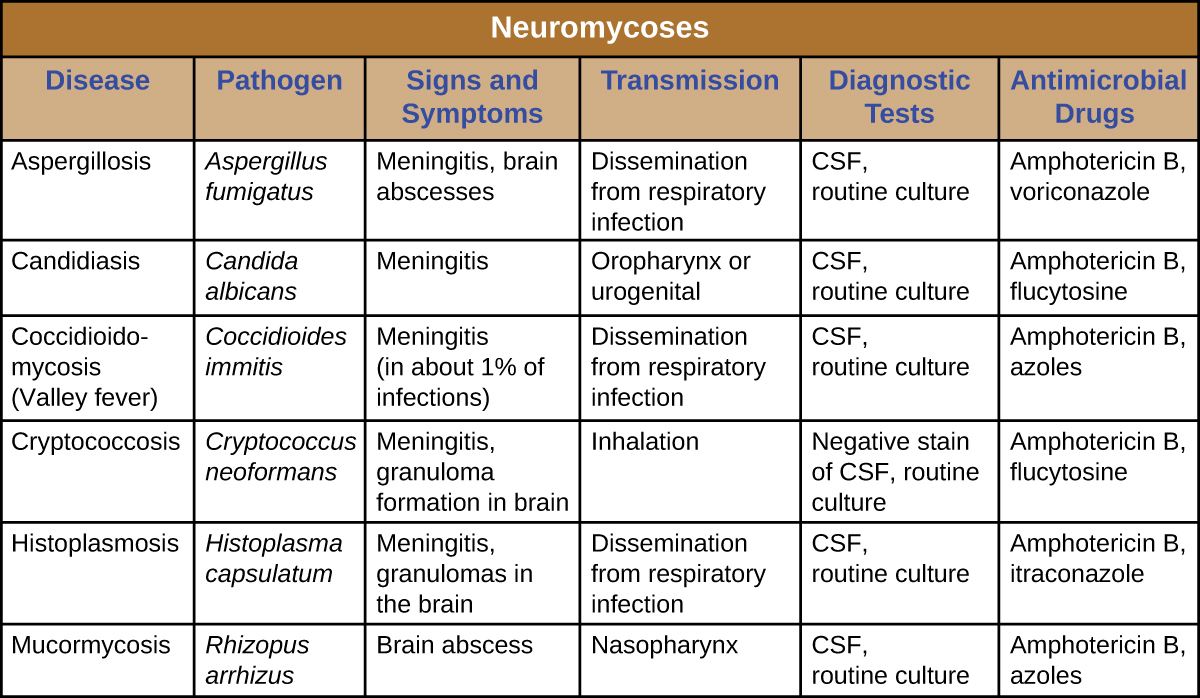
Neuromycoses typically occur only in immunocompromised individuals and usually only invade the nervous system after first infecting a different body system. As such, many diseases that sometimes affect the nervous system have already been discussed in previous chapters. [link] presents some of the most common fungal infections associated with neurological disease. This table includes only the neurological aspects associated with these diseases; it does not include characteristics associated with other body systems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?