| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the developing world, acute viral gastroenteritis is devastating and a leading cause of death for children. Caleb K. King, Roger Glass, Joseph S. Bresee, Christopher Duggan. “Managing Acute Gastroenteritis Among Children: Oral Rehydration, Maintenance, and Nutritional Therapy.” MMWR 52 (2003) RR16: pp. 1–16. http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5216a1.htm. Worldwide, diarrhea is the second leading cause of mortality for children under age five, and 70% of childhood gastroenteritis is viral. Elizabeth Jane Elliott. “Acute Gastroenteritis in Children.” British Medical Journal 334 (2007) 7583: 35–40, doi: 10.1136/bmj.39036.406169.80; S. Ramani and G. Kang. “Viruses Causing Diarrhoea in the Developing World.” Current Opinions in Infectious Diseases 22 (2009) 5: pp. 477–482. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e328330662f; Michael Vincent F Tablang. “Viral Gastroenteritis.” Medscape . http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/176515-overview. As discussed, there are a number of bacteria responsible for diarrhea, but viruses can also cause diarrhea. E. coli and rotavirus are the most common causative agents in the developing world. In this section, we will discuss rotaviruses and other, less common viruses that can also cause gastrointestinal illnesses.
Rotaviruses are double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae . They are responsible for common diarrheal illness, although prevention through vaccination is becoming more common. The virus is primarily spread by the fecal-oral route ( [link] ).
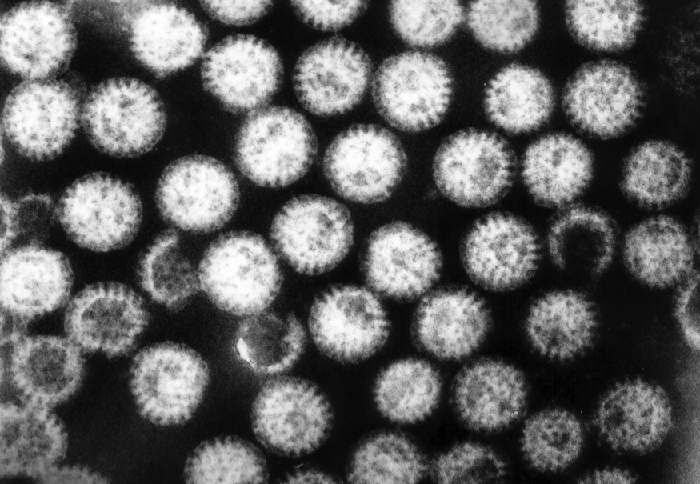
These viruses are widespread in children, especially in day-care centers. The CDC estimates that 95% of children in the United States have had at least one rotavirus infection by the time they reach age five. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Rotavirus,” The Pink Book. Updated September 8, 2015. http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/rota.html. Due to the memory of the body’s immune system, adults who come into contact with rotavirus will not contract the infection or, if they do, are asymptomatic. The elderly, however, are vulnerable to rotavirus infection due to weakening of the immune system with age, so infections can spread through nursing homes and similar facilities. In these cases, the infection may be transmitted from a family member who may have subclinical or clinical disease. The virus can also be transmitted from contaminated surfaces, on which it can survive for some time.
Infected individuals exhibit fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. The virus can survive in the stomach following a meal, but is normally found in the small intestines, particularly the epithelial cells on the villi . Infection can cause food intolerance, especially with respect to lactose. The illness generally appears after an incubation period of about two days and lasts for approximately one week (three to eight days). Without supportive treatment, the illness can cause severe fluid loss, dehydration, and even death. Even with milder illness, repeated infections can potentially lead to malnutrition, especially in developing countries, where rotavirus infection is common due to poor sanitation and lack of access to clean drinking water. Patients (especially children) who are malnourished after an episode of diarrhea are more susceptible to future diarrheal illness, increasing their risk of death from rotavirus infection.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?