| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The early pioneers of microscopy opened a window into the invisible world of microorganisms. But microscopy continued to advance in the centuries that followed. In 1830, Joseph Jackson Lister created an essentially modern light microscope. The 20th century saw the development of microscopes that leveraged nonvisible light, such as fluorescence microscopy, which uses an ultraviolet light source, and electron microscopy, which uses short-wavelength electron beams. These advances led to major improvements in magnification, resolution, and contrast. By comparison, the relatively rudimentary microscopes of van Leeuwenhoek and his contemporaries were far less powerful than even the most basic microscopes in use today. In this section, we will survey the broad range of modern microscopic technology and common applications for each type of microscope.
Many types of microscopes fall under the category of light microscopes , which use light to visualize images. Examples of light microscopes include brightfield microscopes, darkfield microscopes, phase-contrast microscopes, differential interference contrast microscopes, fluorescence microscopes, confocal scanning laser microscopes, and two-photon microscopes. These various types of light microscopes can be used to complement each other in diagnostics and research.
The brightfield microscope , perhaps the most commonly used type of microscope, is a compound microscope with two or more lenses that produce a dark image on a bright background. Some brightfield microscopes are monocular (having a single eyepiece), though most newer brightfield microscopes are binocular (having two eyepieces), like the one shown in [link] ; in either case, each eyepiece contains a lens called an ocular lens . The ocular lenses typically magnify images 10 times (10⨯). At the other end of the body tube are a set of objective lenses on a rotating nosepiece. The magnification of these objective lenses typically ranges from 4⨯ to 100⨯, with the magnification for each lens designated on the metal casing of the lens. The ocular and objective lenses work together to create a magnified image. The total magnification is the product of the ocular magnification times the objective magnification:
For example, if a 40⨯ objective lens is selected and the ocular lens is 10⨯, the total magnification would be
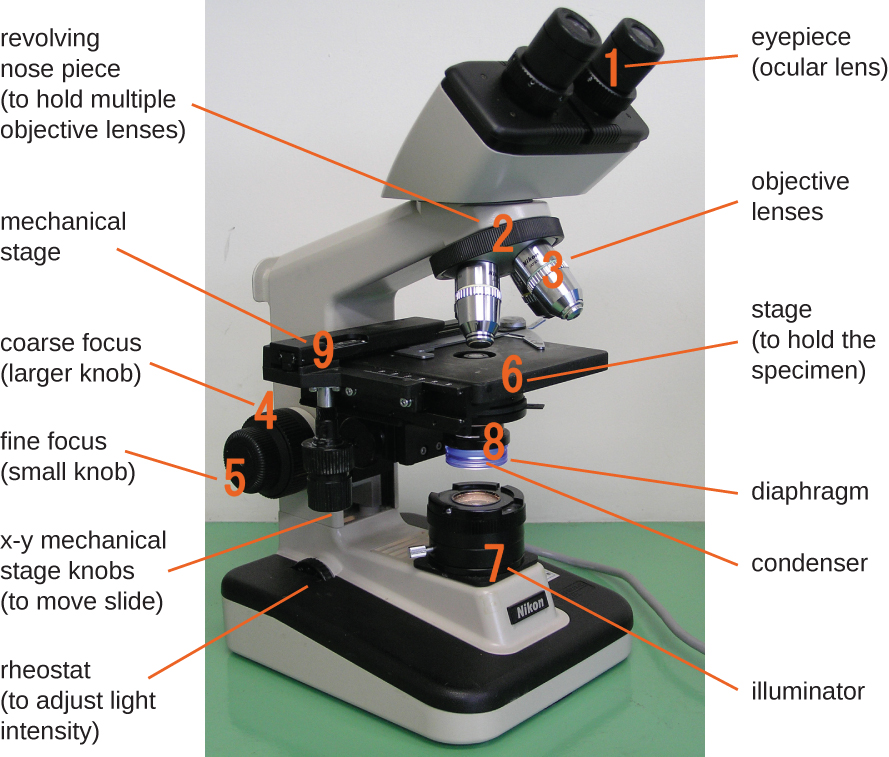
The item being viewed is called a specimen. The specimen is placed on a glass slide, which is then clipped into place on the stage (a platform) of the microscope. Once the slide is secured, the specimen on the slide is positioned over the light using the x-y mechanical stage knobs . These knobs move the slide on the surface of the stage, but do not raise or lower the stage. Once the specimen is centered over the light, the stage position can be raised or lowered to focus the image. The coarse focusing knob is used for large-scale movements with 4⨯ and 10⨯ objective lenses; the fine focusing knob is used for small-scale movements, especially with 40⨯ or 100⨯ objective lenses.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?