| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As discussed in Cellular Defenses , major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules are expressed on the surface of healthy cells, identifying them as normal and “self” to natural killer (NK) cells . MHC molecules also play an important role in the presentation of foreign antigens, which is a critical step in the activation of T cells and thus an important mechanism of the adaptive immune system.
The major histocompatibility complex ( MHC ) is a collection of genes coding for MHC molecules found on the surface of all nucleated cells of the body. In humans, the MHC genes are also referred to as human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes . Mature red blood cells , which lack a nucleus, are the only cells that do not express MHC molecules on their surface.
There are two classes of MHC molecules involved in adaptive immunity, MHC I and MHC II ( [link] ). MHC I molecules are found on all nucleated cells; they present normal self-antigens as well as abnormal or nonself pathogens to the effector T cells involved in cellular immunity. In contrast, MHC II molecules are only found on macrophages , dendritic cells , and B cells ; they present abnormal or nonself pathogen antigens for the initial activation of T cells.
Both types of MHC molecules are transmembrane glycoproteins that assemble as dimers in the cytoplasmic membrane of cells, but their structures are quite different. MHC I molecules are composed of a longer α protein chain coupled with a smaller β 2 microglobulin protein, and only the α chain spans the cytoplasmic membrane. The α chain of the MHC I molecule folds into three separate domains: α 1 , α 2 and α 3 . MHC II molecules are composed of two protein chains (an α and a β chain) that are approximately similar in length. Both chains of the MHC II molecule possess portions that span the plasma membrane, and each chain folds into two separate domains: α 1 and α 2 , and β 1 , and β 2 . In order to present abnormal or non-self-antigens to T cells, MHC molecules have a cleft that serves as the antigen-binding site near the “top” (or outermost) portion of the MHC-I or MHC-II dimer. For MHC I, the antigen-binding cleft is formed by the α 1 and α 2 domains, whereas for MHC II, the cleft is formed by the α 1 and β 1 domains ( [link] ).
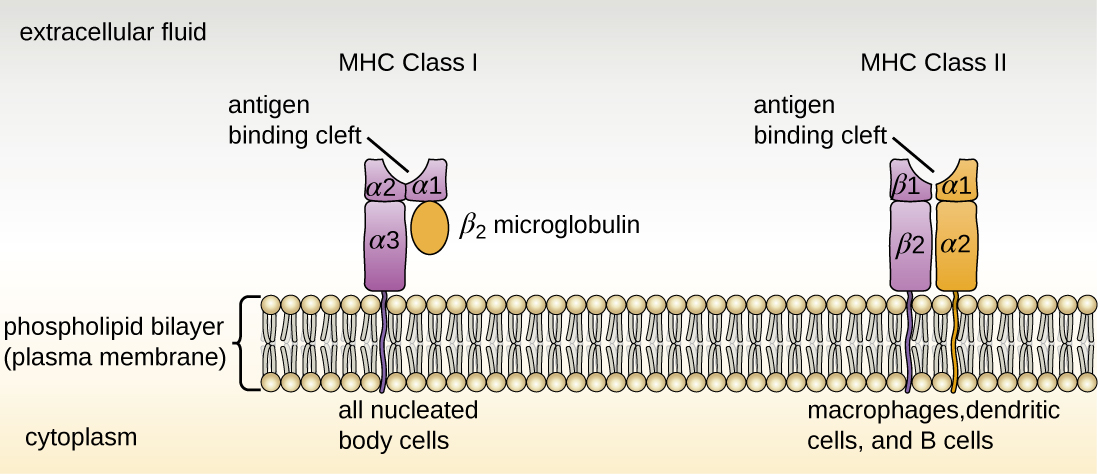
All nucleated cells in the body have mechanisms for processing and presenting antigens in association with MHC molecules. This signals the immune system, indicating whether the cell is normal and healthy or infected with an intracellular pathogen. However, only macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells have the ability to present antigens specifically for the purpose of activating T cells; for this reason, these types of cells are sometimes referred to as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?