| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In addition to physical defenses, the innate nonspecific immune system uses a number of chemical mediators that inhibit microbial invaders. The term “chemical mediators” encompasses a wide array of substances found in various body fluids and tissues throughout the body. Chemical mediators may work alone or in conjunction with each other to inhibit microbial colonization and infection.
Some chemical mediators are endogenously produced, meaning they are produced by human body cells; others are produced exogenously, meaning that they are produced by certain microbes that are part of the microbiome. Some mediators are produced continually, bathing the area in the antimicrobial substance; others are produced or activated primarily in response to some stimulus, such as the presence of microbes.
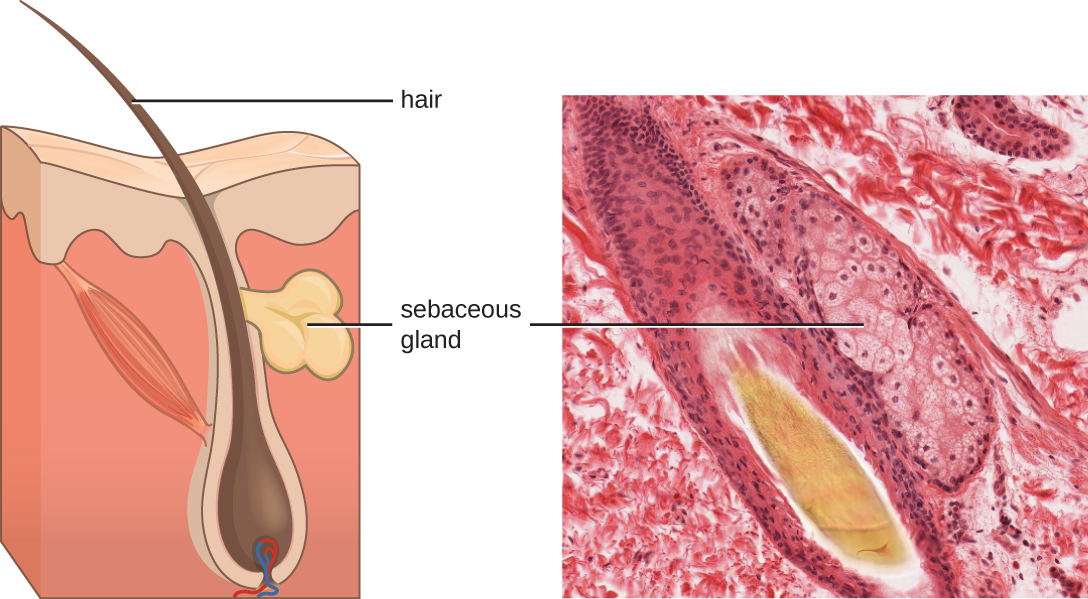
Fluids produced by the skin include examples of both endogenous and exogenous mediators. Sebaceous glands in the dermis secrete an oil called sebum that is released onto the skin surface through hair follicles. This sebum is an endogenous mediator, providing an additional layer of defense by helping seal off the pore of the hair follicle, preventing bacteria on the skin’s surface from invading sweat glands and surrounding tissue ( [link] ). Certain members of the microbiome, such as the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes and the fungus Malassezia , among others, can use lipase enzymes to degrade sebum, using it as a food source. This produces oleic acid , which creates a mildly acidic environment on the surface of the skin that is inhospitable to many pathogenic microbes. Oleic acid is an example of an exogenously produced mediator because it is produced by resident microbes and not directly by body cells.
Environmental factors that affect the microbiota of the skin can have a direct impact on the production of chemical mediators. Low humidity or decreased sebum production, for example, could make the skin less habitable for microbes that produce oleic acid, thus making the skin more susceptible to pathogens normally inhibited by the skin’s low pH. Many skin moisturizers are formulated to counter such effects by restoring moisture and essential oils to the skin.
The digestive tract also produces a large number of chemical mediators that inhibit or kill microbes. In the oral cavity, saliva contains mediators such as lactoperoxidase enzymes, and mucus secreted by the esophagus contains the antibacterial enzyme lysozyme . In the stomach, highly acidic gastric fluid kills most microbes. In the lower digestive tract, the intestines have pancreatic and intestinal enzymes, antibacterial peptides (cryptins), bile produced from the liver, and specialized Paneth cells that produce lysozyme. Together, these mediators are able to eliminate most pathogens that manage to survive the acidic environment of the stomach.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?