| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Both X-rays and gamma rays easily penetrate paper and plastic and can therefore be used to sterilize many packaged materials. In the laboratory, ionizing radiation is commonly used to sterilize materials that cannot be autoclaved, such as plastic Petri dishes and disposable plastic inoculating loops. For clinical use, ionizing radiation is used to sterilize gloves, intravenous tubing, and other latex and plastic items used for patient care. Ionizing radiation is also used for the sterilization of other types of delicate, heat-sensitive materials used clinically, including tissues for transplantation, pharmaceutical drugs, and medical equipment.
In Europe, gamma irradiation for food preservation is widely used, although it has been slow to catch on in the United States (see the Micro Connections box on this topic). Packaged dried spices are also often gamma-irradiated. Because of their ability to penetrate paper, plastic, thin sheets of wood and metal, and tissue, great care must be taken when using X-rays and gamma irradiation. These types of ionizing irradiation cannot penetrate thick layers of iron or lead, so these metals are commonly used to protect humans who may be potentially exposed.
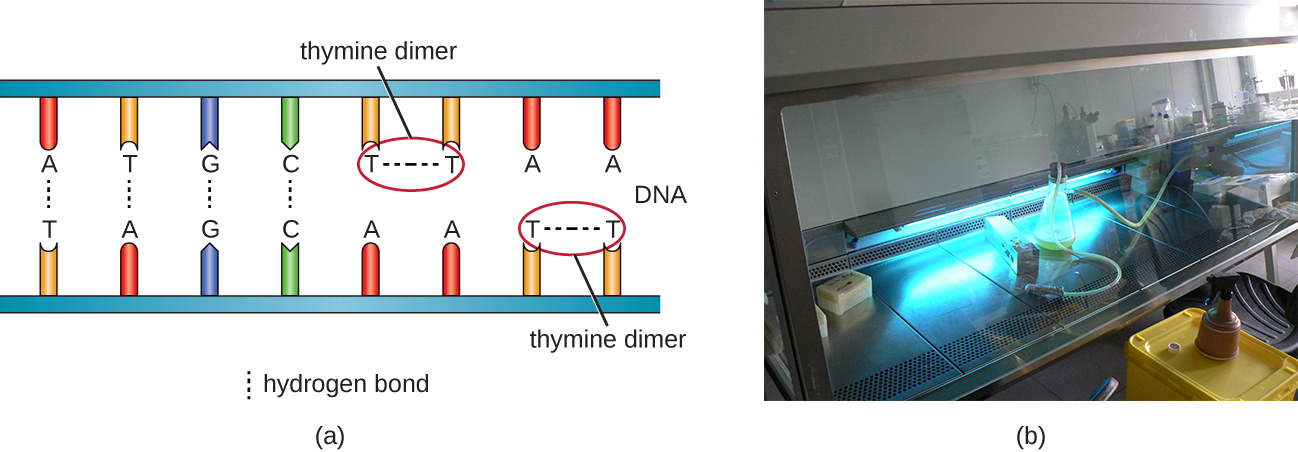
Another type of radiation, nonionizing radiation , is commonly used for sterilization and uses less energy than ionizing radiation. It does not penetrate cells or packaging. Ultraviolet (UV) light is one example; it causes thymine dimer s to form between adjacent thymines within a single strand of DNA ( [link] ). When DNA polymerase encounters the thymine dimer, it does not always incorporate the appropriate complementary nucleotides (two adenines), and this leads to formation of mutations that can ultimately kill microorganisms.
UV light can be used effectively by both consumers and laboratory personnel to control microbial growth. UV lamps are now commonly incorporated into water purification systems for use in homes. In addition, small portable UV lights are commonly used by campers to purify water from natural environments before drinking. Germicidal lamps are also used in surgical suites, biological safety cabinet s, and transfer hoods, typically emitting UV light at a wavelength of 260 nm. Because UV light does not penetrate surfaces and will not pass through plastics or glass, cells must be exposed directly to the light source.
Sunlight has a very broad spectrum that includes UV and visible light. In some cases, sunlight can be effective against certain bacteria because of both the formation of thymine dimers by UV light and by the production of reactive oxygen products induced in low amounts by exposure to visible light.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?