| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Thus far, we have discussed the structure and function of individual pieces of DNA and RNA . In this section, we will discuss how all of an organism’s genetic material—collectively referred to as its genome —is organized inside of the cell. Since an organism’s genetics to a large extent dictate its characteristics, it should not be surprising that organisms differ in the arrangement of their DNA and RNA.
All cellular activities are encoded within a cell’s DNA. The sequence of bases within a DNA molecule represents the genetic information of the cell. Segments of DNA molecules are called gene s, and individual genes contain the instructional code necessary for synthesizing various proteins, enzymes, or stable RNA molecules.
The full collection of genes that a cell contains within its genome is called its genotype . However, a cell does not express all of its genes simultaneously. Instead, it turns on (expresses) or turns off certain genes when necessary. The set of genes being expressed at any given point in time determines the cell’s activities and its observable characteristics, referred to as its phenotype . Genes that are always expressed are known as constitutive genes ; some constitutive genes are known as housekeeping genes because they are necessary for the basic functions of the cell.
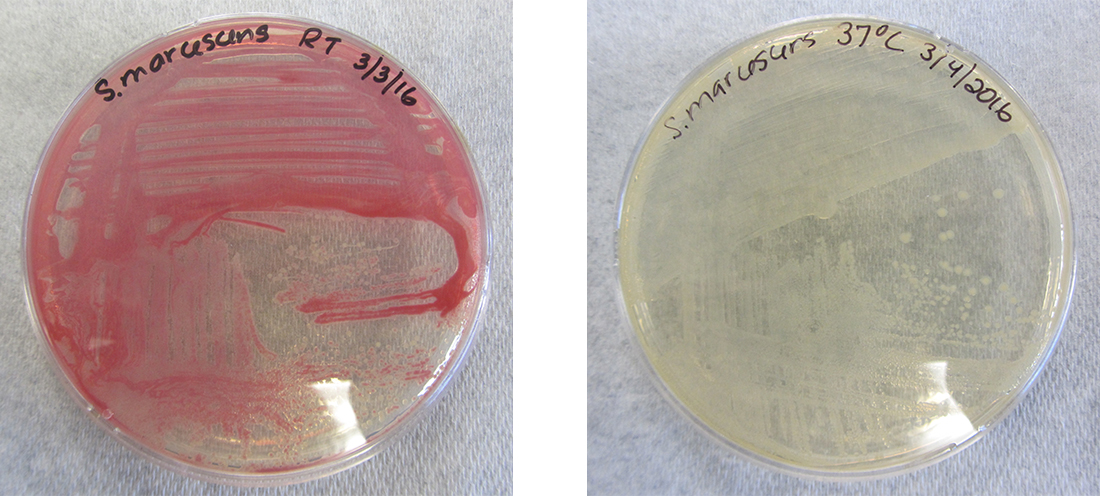
While the genotype of a cell remains constant, the phenotype may change in response to environmental signals (e.g., changes in temperature or nutrient availability) that affect which nonconstitutive genes are expressed. For example, the oral bacterium Streptococcus mutans produces a sticky slime layer that allows it to adhere to teeth, forming dental plaque ; however, the genes that control the production of the slime layer are only expressed in the presence of sucrose (table sugar). Thus, while the genotype of S. mutans is constant, its phenotype changes depending on the presence and absence of sugar in its environment. Temperature can also regulate gene expression . For example, the gram-negative bacterium Serratia marcescens , a pathogen frequently associated with hospital-acquired infections, produces a red pigment at 28 °C but not at 37 °C, the normal internal temperature of the human body ( [link] ).
The vast majority of an organism’s genome is organized into the cell’s chromosomes , which are discrete DNA structures within cells that control cellular activity. Recall that while eukaryotic chromosomes are housed in the membrane-bound nucleus, most prokaryotes contain a single, circular chromosome that is found in an area of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid (see Unique Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells ). A chromosome may contain several thousand genes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?