| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The connection between trade balances and international flows of financial capital is so close that the balance of trade is sometimes described as the balance of payments . Each category of the current account balance involves a corresponding flow of payments between a given country and the rest of the world economy.
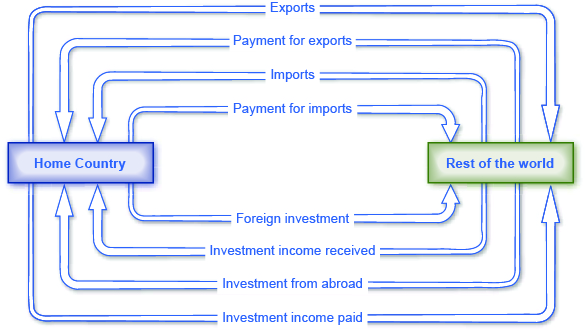
[link] shows the flow of goods and services and payments between one country—the United States in this example—and the rest of the world. The top line shows U.S. exports of goods and services, while the second line shows financial payments from purchasers in other countries back to the U.S. economy. The third line then shows U.S. imports of goods, services, and investment, and the fourth line shows payments from the home economy to the rest of the world. Flow of goods and services (lines one and three) show up in the current account, while flow of funds (lines two and four) are found in the financial account.
The bottom four lines of the [link] show the flow of investment income. In the first of the bottom lines, we see investments made abroad with funds flowing from the home country to rest of the world. Investment income stemming from an investment abroad then runs in the other direction from the rest of the world to the home country. Similarly, we see on the bottom third line, an investment from rest of the world into the home country and investment income (bottom fourth line) flowing from the home country to the rest of the world. The investment income (bottom lines two and four) are found in the current account, while investment to the rest of the world or into the home country (lines one and three) are found in the financial account. Unilateral transfers, the fourth item in the current account, are not shown in this figure.
A current account deficit means that, the country is a net borrower from abroad. Conversely, a positive current account balance means a country is a net lender to the rest of the world. Just like the parable of Robinson and Friday, the lesson is that a trade surplus means an overall outflow of financial investment capital, as domestic investors put their funds abroad, while the deficit in the current account balance is exactly equal to the overall or net inflow of foreign investment capital from abroad.
It is important to recognize that an inflow and outflow of foreign capital does not necessarily refer to a debt that governments owe to other governments, although government debt may be part of the picture. Instead, these international flows of financial capital refer to all of the ways in which private investors in one country may invest in another country—by buying real estate, companies, and financial investments like stocks and bonds.
International flows of goods and services are closely connected to the international flows of financial capital. A current account deficit means that, after taking all the flows of payments from goods, services, and income together, the country is a net borrower from the rest of the world. A current account surplus is the opposite and means the country is a net lender to the rest of the world.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?