| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

The Great Recession of 2008–2009 hit the U.S. economy hard. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the number of unemployed Americans rose from 6.8 million in May 2007 to 15.4 million in October 2009. During that time, the U.S. Census Bureau estimated that approximately 170,000 small businesses closed. Mass layoffs peaked in February 2009 when 326,392 workers were given notice. U.S. productivity and output fell as well. Job losses, declining home values, declining incomes, and uncertainty about the future caused consumption expenditures to decrease. According to the BLS, household spending dropped by 7.8%.
Home foreclosures and the meltdown in U.S. financial markets called for immediate action by Congress, the President, and the Federal Reserve Bank. For example, programs such as the American Restoration and Recovery Act were implemented to help millions of people by providing tax credits for homebuyers, paying “cash for clunkers,” and extending unemployment benefits. From cutting back on spending, filing for unemployment, and losing homes, millions of people were affected by the recession. And while the United States is now on the path to recovery, the impact will be felt for many years to come.
What caused this recession and what prevented the economy from spiraling further into another depression? Policymakers looked to the lessons learned from the Great Depression of the 1930s and to the models developed by John Maynard Keynes to analyze the causes and find solutions to the country’s economic woes. The Keynesian perspective is the subject of this chapter.
In this chapter, you will learn about:
We have learned that the level of economic activity, for example output, employment, and spending, tends to grow over time. In The Keynesian Perspective we learned the reasons for this trend. The Macroeconomic Perspective pointed out that the economy tends to cycle around the long-run trend. In other words, the economy does not always grow at its average growth rate. Sometimes economic activity grows at the trend rate, sometimes it grows more than the trend, sometimes it grows less than the trend, and sometimes it actually declines. You can see this cyclical behavior in [link] .
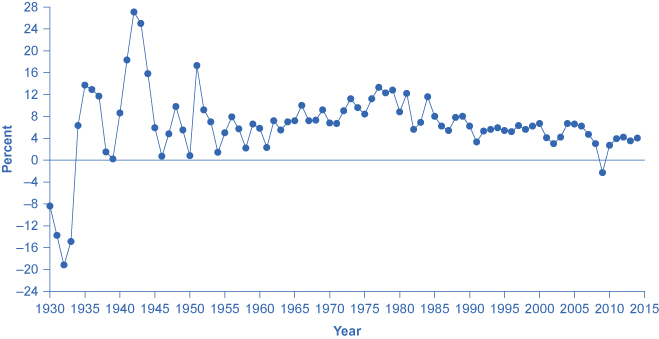
This empirical reality raises two important questions: How can we explain the cycles, and to what extent can they be moderated? This chapter (on the Keynesian perspective) and The Neoclassical Perspective explore those questions from two different points of view, building on what we learned in The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?