| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
We have seen that unemployment varies across times and places. What causes changes in unemployment? There are different answers in the short run and in the long run. Let's look at the short run first.
Let’s make the plausible assumption that in the short run, from a few months to a few years, the quantity of hours that the average person is willing to work for a given wage does not change much, so the labor supply curve does not shift much. In addition, make the standard ceteris paribus assumption that there is no substantial short-term change in the age structure of the labor force, institutions and laws affecting the labor market, or other possibly relevant factors.
One primary determinant of the demand for labor from firms is how they perceive the state of the macro economy . If firms believe that business is expanding, then at any given wage they will desire to hire a greater quantity of labor, and the labor demand curve shifts to the right. Conversely, if firms perceive that the economy is slowing down or entering a recession, then they will wish to hire a lower quantity of labor at any given wage, and the labor demand curve will shift to the left. The variation in unemployment caused by the economy moving from expansion to recession or from recession to expansion (i.e. the business cycle) is known as cyclical unemployment .
From the standpoint of the supply-and-demand model of competitive and flexible labor markets, unemployment represents something of a puzzle. In a supply-and-demand model of a labor market, as illustrated in [link] , the labor market should move toward an equilibrium wage and quantity. At the equilibrium wage (We), the equilibrium quantity (Qe) of labor supplied by workers should be equal to the quantity of labor demanded by employers.
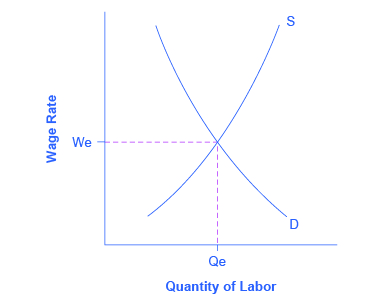
One possibility for unemployment is that people who are unemployed are those who are not willing to work at the current equilibrium wage, say $10 an hour, but would be willing to work at a higher wage, like $20 per hour. The monthly Current Population Survey would count these people as unemployed, because they say they are ready and looking for work (at $20 per hour). But from an economist’s point of view, these people are choosing to be unemployed.
Probably a few people are unemployed because of unrealistic expectations about wages, but they do not represent the majority of the unemployed. Instead, unemployed people often have friends or acquaintances of similar skill levels who are employed, and the unemployed would be willing to work at the jobs and wages similar to what is being received by those people. But the employers of their friends and acquaintances do not seem to be hiring. In other words, these people are involuntarily unemployed. What causes involuntary unemployment ?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?