| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
A change in government budgets may impact private saving. Imagine that people watch government budgets and adjust their savings accordingly. For example, whenever the government runs a budget deficit, people might reason: “Well, a higher budget deficit means that I’m just going to owe more taxes in the future to pay off all that government borrowing, so I’ll start saving now.” If the government runs budget surpluses, people might reason: “With these budget surpluses (or lower budget deficits), interest rates are falling, so that saving is less attractive. Moreover, with a budget surplus the country will be able to afford a tax cut sometime in the future. I won’t bother saving as much now.”
The theory that rational private households might shift their saving to offset government saving or borrowing is known as Ricardian equivalence because the idea has intellectual roots in the writings of the early nineteenth-century economist David Ricardo (1772–1823). If Ricardian equivalence holds completely true, then in the national saving and investment identity, any change in budget deficits or budget surpluses would be completely offset by a corresponding change in private saving. As a result, changes in government borrowing would have no effect at all on either physical capital investment or trade balances.
In practice, the private sector only sometimes and partially adjusts its savings behavior to offset government budget deficits and surpluses. [link] shows the patterns of U.S. government budget deficits and surpluses and the rate of private saving—which includes saving by both households and firms—since 1980. The connection between the two is not at all obvious. In the mid-1980s, for example, government budget deficits were quite large, but there is no corresponding surge of private saving. However, when budget deficits turn to surpluses in the late 1990s, there is a simultaneous decline in private saving. When budget deficits get very large in 2008 and 2009, on the other hand, there is some sign of a rise in saving. A variety of statistical studies based on the U.S. experience suggests that when government borrowing increases by $1, private saving rises by about 30 cents. A World Bank study done in the late 1990s, looking at government budgets and private saving behavior in countries around the world, found a similar result.
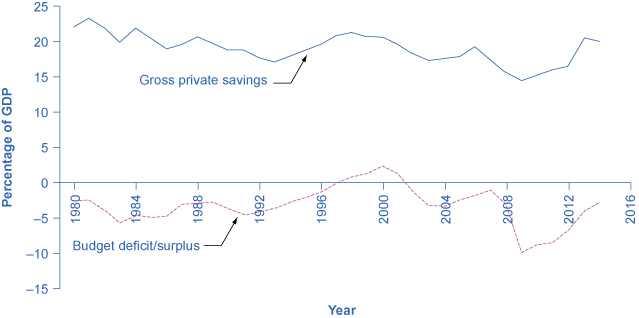
So private saving does increase to some extent when governments run large budget deficits, and private saving falls when governments reduce deficits or run large budget surpluses. However, the offsetting effects of private saving compared to government borrowing are much less than one-to-one. In addition, this effect can vary a great deal from country to country, from time to time, and over the short run and the long run.
If the funding for a larger budget deficit comes from international financial investors, then a budget deficit may be accompanied by a trade deficit. In some countries, this pattern of a twin deficits has set the stage for international financial investors first to send their funds to a country and cause an appreciation of its exchange rate and then to pull their funds out and cause a depreciation of the exchange rate and a financial crisis as well. It depends on whether funding comes from international financial investors.
The theory of Ricardian equivalence holds that changes in government borrowing or saving will be offset by changes in private saving. Thus, higher budget deficits will be offset by greater private saving, while larger budget surpluses will be offset by greater private borrowing. If the theory holds true, then changes in government borrowing or saving would have no effect on private investment in physical capital or on the trade balance. However, empirical evidence suggests that the theory holds true only partially.
Illustrate the concept of Ricardian equivalence using the demand and supply of financial capital graph.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Macroeconomics' conversation and receive update notifications?