| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The South’s dependence on cotton was matched by its dependence on slaves to harvest the cotton. Despite the rhetoric of the Revolution that “all men are created equal,” slavery not only endured in the American republic but formed the very foundation of the country’s economic success. Cotton and slavery occupied a central—and intertwined—place in the nineteenth-century economy.
In 1807, the U.S. Congress abolished the foreign slave trade, a ban that went into effect on January 1, 1808. After this date, importing slaves from Africa became illegal in the United States. While smuggling continued to occur, the end of the international slave trade meant that domestic slaves were in very high demand. Fortunately for Americans whose wealth depended upon the exploitation of slave labor, a fall in the price of tobacco had caused landowners in the Upper South to reduce their production of this crop and use more of their land to grow wheat, which was far more profitable. While tobacco was a labor-intensive crop that required many people to cultivate it, wheat was not. Former tobacco farmers in the older states of Virginia and Maryland found themselves with “surplus” slaves whom they were obligated to feed, clothe, and shelter. Some slaveholders responded to this situation by freeing slaves; far more decided to sell their excess bondsmen. Virginia and Maryland therefore took the lead in the domestic slave trade , the trading of slaves within the borders of the United States.
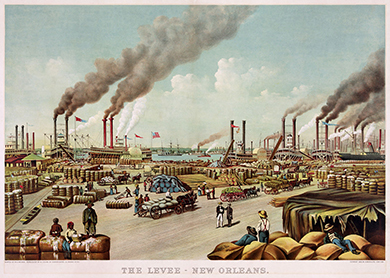
The domestic slave trade offered many economic opportunities for white men. Those who sold their slaves could realize great profits, as could the slave brokers who served as middlemen between sellers and buyers. Other white men could benefit from the trade as owners of warehouses and pens in which slaves were held, or as suppliers of clothing and food for slaves on the move. Between 1790 and 1859, slaveholders in Virginia sold more than half a million slaves. In the early part of this period, many of these slaves were sold to people living in Kentucky, Tennessee, and North and South Carolina. By the 1820s, however, people in Kentucky and the Carolinas had begun to sell many of their slaves as well. Maryland slave dealers sold at least 185,000 slaves. Kentucky slaveholders sold some seventy-one thousand individuals. Most of the slave traders carried these slaves further south to Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi. New Orleans, the hub of commerce, boasted the largest slave market in the United States and grew to become the nation’s fourth-largest city as a result. Natchez, Mississippi, had the second-largest market. In Virginia, Maryland, the Carolinas, and elsewhere in the South, slave auctions happened every day.
All told, the movement of slaves in the South made up one of the largest forced internal migrations in the United States. In each of the decades between 1820 and 1860, about 200,000 people were sold and relocated. The 1800 census recorded over one million African Americans, of which nearly 900,000 were slaves. By 1860, the total number of African Americans increased to 4.4 million, and of that number, 3.95 million were held in bondage. For many slaves, the domestic slave trade incited the terror of being sold away from family and friends.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?