| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the New World, the institution of slavery assumed a new aspect when the mercantilist system demanded a permanent, identifiable, and plentiful labor supply. African slaves were both easily identified (by their skin color) and plentiful, because of the thriving slave trade. This led to a race-based slavery system in the New World unlike any bondage system that had come before. Initially, the Spanish tried to force Indians to farm their crops. Most Spanish and Portuguese settlers coming to the New World were gentlemen and did not perform physical labor. They came to “serve God, but also to get rich,” as noted by Bernal Díaz del Castillo. However, enslaved natives tended to sicken or die from disease or from the overwork and cruel treatment they were subjected to, and so the indigenous peoples proved not to be a dependable source of labor. Although he later repented of his ideas, the great defender of the Indians, Bartolomé de Las Casas, seeing the near extinction of the native population, suggested the Spanish send black (and white) laborers to the Indies. These workers proved hardier, and within fifty years, a change took place: The profitability of the African slave trade, coupled with the seemingly limitless number of potential slaves and the Catholic Church’s denunciation of the enslavement of Christians, led race to become a dominant factor in the institution of slavery.
In the English colonies along the Atlantic coast, indentured servants initially filled the need for labor in the North, where family farms were the norm. In the South, however, labor-intensive crops such as tobacco, rice, and indigo prevailed, and eventually the supply of indentured servants was insufficient to meet the demand. These workers served only for periods of three to seven years before being freed; a more permanent labor supply was needed. Thus, whereas in Africa permanent, inherited slavery was unknown, and children of those bound in slavery to the tribe usually were free and intermarried with their captors, this changed in the Americas; slavery became permanent, and children born to slaves became slaves. This development, along with slavery’s identification with race, forever changed the institution and shaped its unique character in the New World.
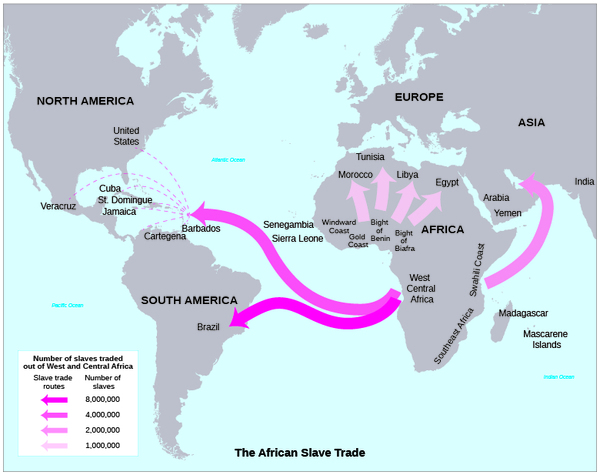
Slavery has a long history. The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle posited that some peoples were homunculi , or humanlike but not really people—for instance, if they did not speak Greek. Both the Bible and the Koran sanction slavery. Vikings who raided from Ireland to Russia brought back slaves of all nationalities. During the Middle Ages, traders from the interior of Africa brought slaves along well-established routes to sell them along the Mediterranean coast. Initially, slavers also brought European slaves to the Caribbean. Many of these were orphaned or homeless children captured in the cities of Ireland. The question is, when did slavery become based on race? This appears to have developed in the New World, with the introduction of gruelingly labor-intensive crops such as sugar and coffee. Unable to fill their growing need from the ranks of prisoners or indentured servants, the European colonists turned to African laborers. The Portuguese, although seeking a trade route to India, also set up forts along the West African coast for the purpose of exporting slaves to Europe. Historians believe that by the year 1500, 10 percent of the population of Lisbon and Seville consisted of black slaves. Because of the influence of the Catholic Church, which frowned on the enslavement of Christians, European slave traders expanded their reach down the coast of Africa.
When Europeans settled Brazil, the Caribbean, and North America, they thus established a system of racially based slavery. Here, the need for a massive labor force was greater than in western Europe. The land was ripe for growing sugar, coffee, rice, and ultimately cotton. To fulfill the ever-growing demand for these crops, large plantations were created. The success of these plantations depended upon the availability of a permanent, plentiful, identifiable, and skilled labor supply. As Africans were already familiar with animal husbandry as well as farming, had an identifying skin color, and could be readily supplied by the existing African slave trade, they proved the answer to this need. This process set the stage for the expansion of New World slavery into North America.
Before 1492, Africa, like the Americas, had experienced the rise and fall of many cultures, but the continent did not develop a centralized authority structure. African peoples practiced various forms of slavery, all of which differed significantly from the racial slavery that ultimately developed in the New World. After the arrival of Islam and before the Portuguese came to the coast of West Africa in 1444, Muslims controlled the slave trade out of Africa, which expanded as European powers began to colonize the New World. Driven by a demand for labor, slavery in the Americas developed a new form: It was based on race, and the status of slave was both permanent and inherited.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?