| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
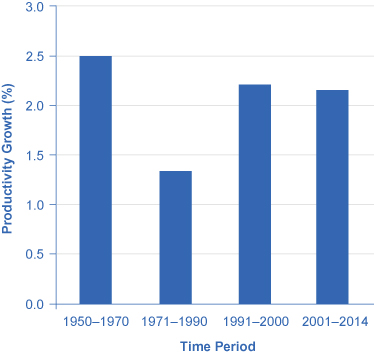
In recent years a controversy has been brewing among economists about the resurgence of U.S. productivity in the second half of the 1990s. One school of thought argues that the United States had developed a “new economy” based on the extraordinary advances in communications and information technology of the 1990s. The most optimistic proponents argue that it would generate higher average productivity growth for decades to come. The pessimists, on the other hand, argue that even five or ten years of stronger productivity growth does not prove that higher productivity will last for the long term. It is hard to infer anything about long-term productivity trends during the later part of the 2000s, because the steep recession of 2008–2009, with its sharp but not completely synchronized declines in output and employment, complicates any interpretation. While productivity growth was high in 2009 and 2010 (around 3%), it has slowed down since then.
Productivity growth is also closely linked to the average level of wages. Over time, the amount that firms are willing to pay workers will depend on the value of the output those workers produce. If a few employers tried to pay their workers less than what those workers produced, then those workers would receive offers of higher wages from other profit-seeking employers. If a few employers mistakenly paid their workers more than what those workers produced, those employers would soon end up with losses. In the long run, productivity per hour is the most important determinant of the average wage level in any economy. To learn how to compare economies in this regard, follow the steps in the following Work It Out feature.
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) tracks data on the annual growth rate of real GDP per hour worked. You can find these data on the OECD data webpage “Labour productivity growth in the total economy” at this website.
Step 1. Visit the OECD website given above and select two countries to compare.
Step 2. On the drop-down menu “Variable,” select “Real GDP, Annual Growth, in percent” and record the data for the countries you have chosen for the five most recent years.
Step 3. Go back to the drop-down menu and select “Real GDP per Hour Worked, Annual Growth Rate, in percent” and select data for the same years for which you selected GDP data.
Step 4. Compare real GDP growth for both countries. [link] provides an example of a comparison between Australia and Belgium.
| Australia | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
| Real GDP Growth (%) | 0.1% | 1.0% | 2.2% | 0.8 | 0.7% |
| Real GDP Growth/Hours Worked (%) | 1.9% | –0.3% | 2.4% | 3.3% | 1.4% |
| Belgium | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
| Real GDP Growth (%) | –3.4 | 1.6 | 0.8 | –0.6 | –0.2 |
| Real GDP Growth/Hours Worked (%) | –1.3 | –1.4 | –0.5 | –0.3 | 0.3 |
Step 5. Consider the many factors can affect growth. For example, one factor that may have affected Australia is its isolation from Europe, which may have insulated the country from the effects of the global recession. In Belgium’s case, the global recession seems to have had an impact on both GDP and real GDP per hours worked between 2009 and 2013, though productivity does seem to be recovering.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?