| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Whenever there are expansions in an industry, costs of production for the existing and new firms could either stay the same, increase, or even decrease. Therefore, we can categorize an industry as being (1) a constant cost industry (as demand increases, the cost of production for firms stays the same), (2) an increasing cost industry (as demand increases, the cost of production for firms increases), or (3) a decreasing cost industry (as demand increases the costs of production for the firms decreases).
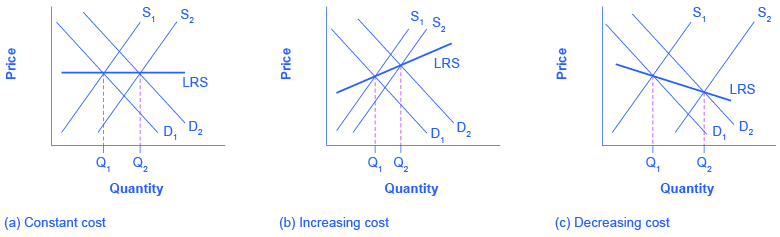
For a constant cost industry , whenever there is an increase in market demand and price, then the supply curve shifts to the right with new firms’ entry and stops at the point where the new long-run equilibrium intersects at the same market price as before. But why will costs remain the same? In this type of industry, the supply curve is very elastic. Firms can easily supply any quantity that consumers demand. In addition, there is a perfectly elastic supply of inputs—firms can easily increase their demand for employees, for example, with no increase to wages. Tying in to our Bring it Home discussion, an increased demand for ethanol in recent years has caused the demand for corn to increase. Consequently, many farmers switched from growing wheat to growing corn. Agricultural markets are generally good examples of constant cost industries.
For an increasing cost industry , as the market expands, the old and new firms experience increases in their costs of production, which makes the new zero-profit level intersect at a higher price than before. Here companies may have to deal with limited inputs, such as skilled labor. As the demand for these workers rise, wages rise and this increases the cost of production for all firms. The industry supply curve in this type of industry is more inelastic.
For a decreasing cost industry , as the market expands, the old and new firms experience lower costs of production, which makes the new zero-profit level intersect at a lower price than before. In this case, the industry and all the firms in it are experiencing falling average total costs. This can be due to an improvement in technology in the entire industry or an increase in the education of employees. High tech industries may be a good example of a decreasing cost market.
[link] (a) presents the case of an adjustment process in a constant cost industry. Whenever there are output expansions in this type of industry, the long-run outcome implies more output produced at exactly the same original price. Note that supply was able to increase to meet the increased demand. When we join the before and after long-run equilibriums, the resulting line is the long run supply (LRS) curve in perfectly competitive markets. In this case, it is a flat curve. [link] (b) and [link] (c) present the cases for an increasing cost and decreasing cost industry, respectively. For an increasing cost industry, the LRS is upward sloping, while for a decreasing cost industry, the LRS is downward sloping.
In the long run, firms will respond to profits through a process of entry, where existing firms expand output and new firms enter the market. Conversely, firms will react to losses in the long run through a process of exit, in which existing firms reduce output or cease production altogether. Through the process of entry in response to profits and exit in response to losses, the price level in a perfectly competitive market will move toward the zero-profit point, where the marginal cost curve crosses the AC curve, at the minimum of the average cost curve.
The long-run supply curve shows the long-run output supplied by firms in three different types of industries: constant cost, increasing cost, and decreasing cost.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?