| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
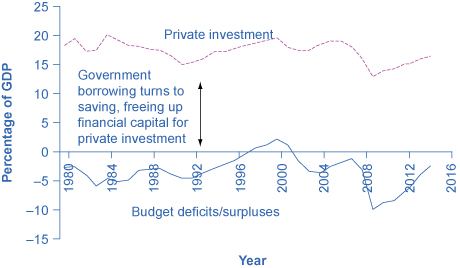
This argument does not claim that a government's budget deficits will exactly shadow its national rate of private investment; after all, private saving and inflows of foreign financial investment must also be taken into account. In the mid-1980s, for example, government budget deficits increased substantially without a corresponding drop off in private investment. In 2009, nonresidential private fixed investment dropped by $300 billion from its previous level of $1,941 billion in 2008, primarily because, during a recession, firms lack both the funds and the incentive to invest. Investment growth between 2009 and 2014 averaged approximately 5.9% to $2,210.5 billion—only slightly above its 2008 level, according to the Bureau of Economic Analysis. During that same period, interest rates dropped from 3.94% to less than a quarter percent as the Federal Reserve took dramatic action to prevent a depression by increasing the money supply through lowering short-term interest rates. The "crowding out" of private investment due to government borrowing to finance expenditures appears to have been suspended during the Great Recession. However, as the economy improves and interest rates rise, borrowing by the government may potentially create pressure on interest rates.
Assume that government borrowing of substantial amounts will have an effect on the quantity of private investment. How will this affect interest rates in financial markets? In [link] , the original equilibrium (E 0 ) where the demand curve (D 0 ) for financial capital intersects with the supply curve (S 0 ) occurs at an interest rate of 5% and an equilibrium quantity equal to 20% of GDP. However, as the government budget deficit increases, the demand curve for financial capital shifts from D 0 to D 1 . The new equilibrium (E 1 ) occurs at an interest rate of 6% and an equilibrium quantity of 21% of GDP.
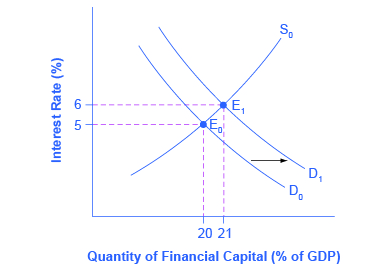
A survey of economic studies on the connection between government borrowing and interest rates in the U.S. economy suggests that an increase of 1% in the budget deficit will lead to a rise in interest rates of between 0.5 and 1.0%, other factors held equal. In turn, a higher interest rate tends to discourage firms from making physical capital investments. One reason government budget deficits crowd out private investment, therefore, is the increase in interest rates. There are, however, economic studies that show a limited connection between the two (at least in the United States), but as the budget deficit grows, the dangers of rising interest rates become more real.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?