| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Exchange rates can fluctuate a great deal in the short run. As yet one more example, the Indian rupee moved from 39 rupees/dollar in February 2008 to 51 rupees/dollar in March 2009, a decline of more than one-fourth in the value of the rupee on foreign exchange markets. [link] earlier showed that even two economically developed neighboring economies like the United States and Canada can see significant movements in exchange rates over a few years. For firms that depend on export sales, or firms that rely on imported inputs to production, or even purely domestic firms that compete with firms tied into international trade—which in many countries adds up to half or more of a nation’s GDP—sharp movements in exchange rates can lead to dramatic changes in profits and losses. So, a central bank may desire to keep exchange rates from moving too much as part of providing a stable business climate, where firms can focus on productivity and innovation, not on reacting to exchange rate fluctuations.
One of the most economically destructive effects of exchange rate fluctuations can happen through the banking system. Most international loans are measured in a few large currencies, like U.S. dollars, European euros, and Japanese yen. In countries that do not use these currencies, banks often borrow funds in the currencies of other countries, like U.S. dollars, but then lend in their own domestic currency. The left-hand chain of events in [link] shows how this pattern of international borrowing can work. A bank in Thailand borrows one million in U.S. dollars. Then the bank converts the dollars to its domestic currency—in the case of Thailand, the currency is the baht—at a rate of 40 baht/dollar. The bank then lends the baht to a firm in Thailand. The business repays the loan in baht, and the bank converts it back to U.S. dollars to pay off its original U.S. dollar loan.
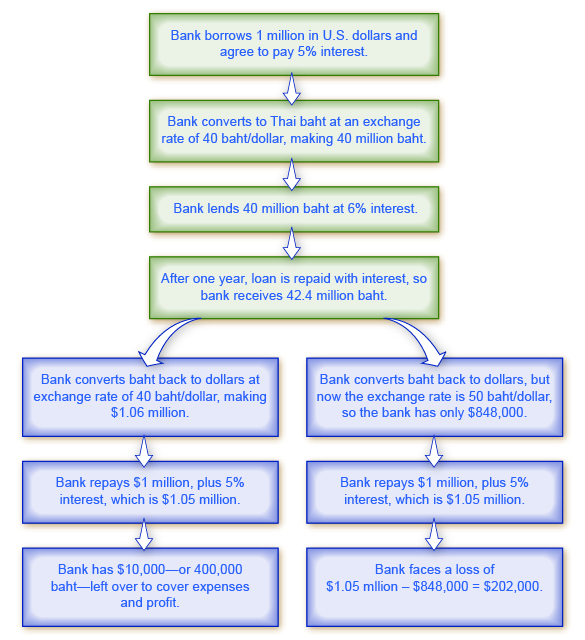
This process of borrowing in a foreign currency and lending in a domestic currency can work just fine, as long as the exchange rate does not shift. In the scenario outlined, if the dollar strengthens and the baht weakens, a problem arises. The right-hand chain of events in [link] illustrates what happens when the baht unexpectedly weakens from 40 baht/dollar to 50 baht/dollar. The Thai firm still repays the loan in full to the bank. But because of the shift in the exchange rate, the bank cannot repay its loan in U.S. dollars. (Of course, if the exchange rate had changed in the other direction, making the Thai currency stronger, the bank could have realized an unexpectedly large profit.)
In 1997–1998, countries across eastern Asia, like Thailand, Korea, Malaysia, and Indonesia, experienced a sharp depreciation of their currencies, in some cases 50% or more. These countries had been experiencing substantial inflows of foreign investment capital , with bank lending increasing by 20% to 30% per year through the mid-1990s. When their exchange rates depreciated, the banking systems in these countries were bankrupt. Argentina experienced a similar chain of events in 2002. When the Argentine peso depreciated, Argentina’s banks found themselves unable to pay back what they had borrowed in U.S. dollars.
Banks play a vital role in any economy in facilitating transactions and in making loans to firms and consumers. When most of a country’s largest banks become bankrupt simultaneously, a sharp decline in aggregate demand and a deep recession results. Since the main responsibilities of a central bank are to control the money supply and to ensure that the banking system is stable, a central bank must be concerned about whether large and unexpected exchange rate depreciation will drive most of the country’s existing banks into bankruptcy. For more on this concern, return to the chapter on The International Trade and Capital Flows .
Every nation would prefer a stable exchange rate to facilitate international trade and reduce the degree of risk and uncertainty in the economy. However, a nation may sometimes want a weaker exchange rate to stimulate aggregate demand and reduce a recession, or a stronger exchange rate to fight inflation. The country must also be concerned that rapid movements from a weak to a strong exchange rate may cripple its export industries, while rapid movements from a strong to a weak exchange rate can cripple its banking sector. In short, every choice of an exchange rate—whether it should be stronger or weaker, or fixed or changing—represents potential tradeoffs.
A central bank will be concerned about the exchange rate for several reasons. Exchange rates will affect imports and exports, and thus affect aggregate demand in the economy. Fluctuations in exchange rates may cause difficulties for many firms, but especially banks. The exchange rate may accompany unsustainable flows of international financial capital.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?