| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
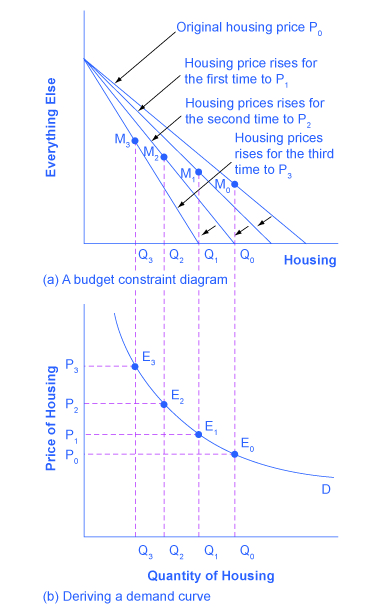
So, as the price of housing rises, the budget constraint shifts to the left, and the quantity consumed of housing falls, ceteris paribus (meaning, with all other things being the same). This relationship—the price of housing rising from P 0 to P 1 to P 2 to P 3 , while the quantity of housing demanded falls from Q 0 to Q 1 to Q 2 to Q 3 —is graphed on the demand curve in [link] (b). Indeed, the vertical dashed lines stretching between the top and bottom of [link] show that the quantity of housing demanded at each point is the same in both (a) and (b). The shape of a demand curve is ultimately determined by the underlying choices about maximizing utility subject to a budget constraint. And while economists may not be able to measure “utils,” they can certainly measure price and quantity demanded.
The budget constraint framework for making utility-maximizing choices offers a reminder that people can react to a change in price or income in a range of different ways. For example, in the winter months of 2005, costs for heating homes increased significantly in many parts of the country as prices for natural gas and electricity soared, due in large part to the disruption caused by Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Some people reacted by reducing the quantity demanded of energy; for example, by turning down the thermostats in their homes by a few degrees and wearing a heavier sweater inside. Even so, many home heating bills rose, so people adjusted their consumption in other ways, too. As you learned in the chapter on Elasticity , the short run demand for home heating is generally inelastic. Each household cut back on what it valued least on the margin; for some it might have been some dinners out, or a vacation, or postponing buying a new refrigerator or a new car. Indeed, sharply higher energy prices can have effects beyond the energy market, leading to a widespread reduction in purchasing throughout the rest of the economy.
A similar issue arises when the government imposes taxes on certain products, like it does on gasoline, cigarettes, and alcohol. Say that a tax on alcohol leads to a higher price at the liquor store, the higher price of alcohol causes the budget constraint to pivot left, and consumption of alcoholic beverages is likely to decrease. However, people may also react to the higher price of alcoholic beverages by cutting back on other purchases. For example, they might cut back on snacks at restaurants like chicken wings and nachos. It would be unwise to assume that the liquor industry is the only one affected by the tax on alcoholic beverages. Read the next Clear It Up to learn about how buying decisions are influenced by who controls the household income.
In the mid-1970s, the United Kingdom made an interesting policy change in its “child allowance” policy. This program provides a fixed amount of money per child to every family, regardless of family income. Traditionally, the child allowance had been distributed to families by withholding less in taxes from the paycheck of the family wage earner—typically the father in this time period. The new policy instead provided the child allowance as a cash payment to the mother. As a result of this change, households have the same level of income and face the same prices in the market, but the money is more likely to be in the purse of the mother than in the wallet of the father.
Should this change in policy alter household consumption patterns? Basic models of consumption decisions, of the sort examined in this chapter, assume that it does not matter whether the mother or the father receives the money, because both parents seek to maximize the utility of the family as a whole. In effect, this model assumes that everyone in the family has the same preferences.
In reality, the share of income controlled by the father or the mother does affect what the household consumes. When the mother controls a larger share of family income a number of studies, in the United Kingdom and in a wide variety of other countries, have found that the family tends to spend more on restaurant meals, child care, and women’s clothing, and less on alcohol and tobacco. As the mother controls a larger share of household resources, children’s health improves, too. These findings suggest that when providing assistance to poor families, in high-income countries and low-income countries alike, the monetary amount of assistance is not all that matters: it also matters which member of the family actually receives the money.
The budget constraint framework serves as a constant reminder to think about the full range of effects that can arise from changes in income or price, not just effects on the one product that might seem most immediately affected.
The budget constraint framework suggest that when income or price changes, a range of responses are possible. When income rises, households will demand a higher quantity of normal goods, but a lower quantity of inferior goods. When the price of a good rises, households will typically demand less of that good—but whether they will demand a much lower quantity or only a slightly lower quantity will depend on personal preferences. Also, a higher price for one good can lead to more or less of the other good being demanded.
If a 10% decrease in the price of one product that you buy causes an 8% increase in quantity demanded of that product, will another 10% decrease in the price cause another 8% increase (no more and no less) in quantity demanded?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?