| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Visit this website to read FAQs on the BEA site. You can even email your own questions!
When thinking about the demand for domestically produced goods in a global economy, it is important to count spending on exports—domestically produced goods that are sold abroad. By the same token, we must also subtract spending on imports—goods produced in other countries that are purchased by residents of this country. The net export component of GDP is equal to the dollar value of exports (X) minus the dollar value of imports (M), (X – M). The gap between exports and imports is called the trade balance . If a country’s exports are larger than its imports, then a country is said to have a trade surplus . In the United States, exports typically exceeded imports in the 1960s and 1970s, as shown in [link] (b).
Since the early 1980s, imports have typically exceeded exports, and so the United States has experienced a trade deficit in most years. Indeed, the trade deficit grew quite large in the late 1990s and in the mid-2000s. [link] (b) also shows that imports and exports have both risen substantially in recent decades, even after the declines during the Great Recession between 2008 and 2009. As noted before, if exports and imports are equal, foreign trade has no effect on total GDP. However, even if exports and imports are balanced overall, foreign trade might still have powerful effects on particular industries and workers by causing nations to shift workers and physical capital investment toward one industry rather than another.
Based on these four components of demand, GDP can be measured as:
Understanding how to measure GDP is important for analyzing connections in the macro economy and for thinking about macroeconomic policy tools.
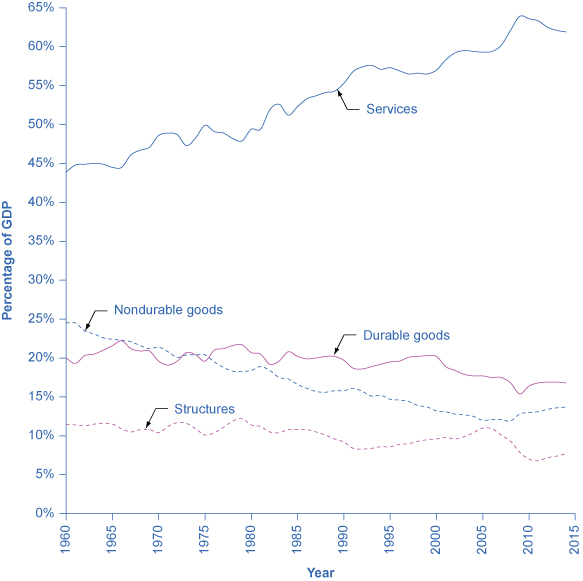
Everything that is purchased must be produced first. [link] breaks down what is produced into five categories: durable goods , nondurable goods , services , structures , and the change in inventories . Before going into detail about these categories, notice that total GDP measured according to what is produced is exactly the same as the GDP measured by looking at the five components of demand. [link] provides a visual representation of this information.
| Components of GDP on the Supply Side (in trillions of dollars) | Percentage of Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Goods | ||
| Durable goods | $2.9 | 16.7% |
| Nondurable goods | $2.3 | 13.2% |
| Services | $10.8 | 62.1% |
| Structures | $1.3 | 7.4% |
| Change in inventories | $0.1 | 0.6% |
| Total GDP | $17.4 | 100% |

Since every market transaction must have both a buyer and a seller, GDP must be the same whether measured by what is demanded or by what is produced. [link] shows these components of what is produced, expressed as a percentage of GDP, since 1960.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?