| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Exchange rate policies come in a range of different forms listed in [link] : let the foreign exchange market determine the exchange rate; let the market set the value of the exchange rate most of the time, but have the central bank sometimes intervene to prevent fluctuations that seem too large; have the central bank guarantee a specific exchange rate; or share a currency with other countries. Let’s discuss each type of exchange rate policy and its tradeoffs.
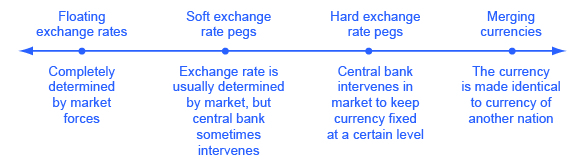
A policy which allows the foreign exchange market to set exchange rates is referred to as a floating exchange rate . The U.S. dollar is a floating exchange rate, as are the currencies of about 40% of the countries in the world economy. The major concern with this policy is that exchange rates can move a great deal in a short time.
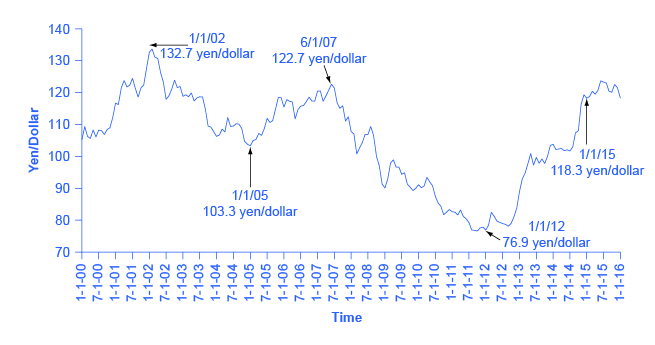
Consider the U.S. exchange rate expressed in terms of another fairly stable currency, the Japanese yen, as shown in [link] . On January 1, 2002, the exchange rate was 133 yen/dollar. On January 1, 2005, it was 103 yen/dollar. On June 1, 2007, it was 122 yen/dollar, on January 1, 2012, it was 77 yen per dollar, and on March 1, 2015, it was 120 yen per dollar. As investor sentiment swings back and forth, driving exchange rates up and down, exporters, importers, and banks involved in international lending are all affected. At worst, large movements in exchange rates can drive companies into bankruptcy or trigger a nationwide banking collapse. But even in the moderate case of the yen/dollar exchange rate, these movements of roughly 30 percent back and forth impose stress on both economies as firms must alter their export and import plans to take the new exchange rates into account. Especially in smaller countries where international trade is a relatively large share of GDP, exchange rate movements can rattle their economies.
However, movements of floating exchange rates have advantages, too. After all, prices of goods and services rise and fall throughout a market economy, as demand and supply shift. If an economy experiences strong inflows or outflows of international financial capital, or has relatively high inflation, or if it experiences strong productivity growth so that purchasing power changes relative to other economies, then it makes economic sense for the exchange rate to shift as well.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?