| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
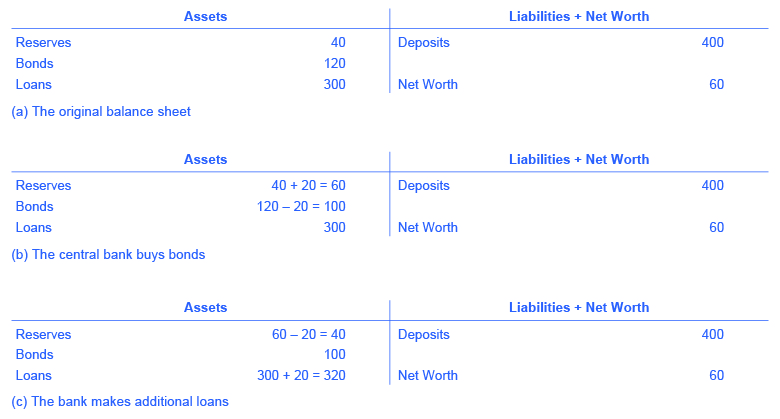
Where did the Federal Reserve get the $20 million that it used to purchase the bonds ? A central bank has the power to create money. In practical terms, the Federal Reserve would write a check to Happy Bank, so that Happy Bank can have that money credited to its bank account at the Federal Reserve. In truth, the Federal Reserve created the money to purchase the bonds out of thin air—or with a few clicks on some computer keys.
Open market operations can also reduce the quantity of money and loans in an economy. [link] (a) shows the balance sheet of Happy Bank before the central bank sells bonds in the open market. When Happy Bank purchases $30 million in bonds, Happy Bank sends $30 million of its reserves to the central bank, but now holds an additional $30 million in bonds, as shown in [link] (b). However, Happy Bank wants to hold $40 million in reserves, as in [link] (a), so it will adjust down the quantity of its loans by $30 million, to bring its reserves back to the desired level, as shown in [link] (c). In practical terms, a bank can easily reduce its quantity of loans. At any given time, a bank is receiving payments on loans that it made previously and also making new loans. If the bank just slows down or briefly halts making new loans, and instead adds those funds to its reserves, then its overall quantity of loans will decrease. A decrease in the quantity of loans also means fewer deposits in other banks, and other banks reducing their lending as well, as the money multiplier discussed in Money and Banking takes effect. And what about all those bonds? How do they affect the money supply? Read the following Clear It Up feature for the answer.
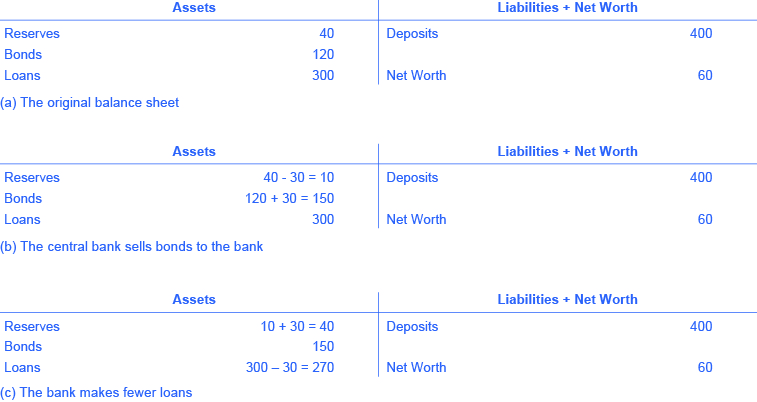
Is it a sale of bonds by the central bank which increases bank reserves and lowers interest rates or is it a purchase of bonds by the central bank? The easy way to keep track of this is to treat the central bank as being outside the banking system. When a central bank buys bonds, money is flowing from the central bank to individual banks in the economy, increasing the supply of money in circulation. When a central bank sells bonds, then money from individual banks in the economy is flowing into the central bank—reducing the quantity of money in the economy.
A second method of conducting monetary policy is for the central bank to raise or lower the reserve requirement , which, as we noted earlier, is the percentage of each bank’s deposits that it is legally required to hold either as cash in their vault or on deposit with the central bank. If banks are required to hold a greater amount in reserves , they have less money available to lend out. If banks are allowed to hold a smaller amount in reserves, they will have a greater amount of money available to lend out.
In early 2015, the Federal Reserve required banks to hold reserves equal to 0% of the first $14.5 million in deposits, then to hold reserves equal to 3% of the deposits up to $103.6 million, and 10% of any amount above $103.6 million. Small changes in the reserve requirements are made almost every year. For example, the $103.6 million dividing line is sometimes bumped up or down by a few million dollars. In practice, large changes in reserve requirements are rarely used to execute monetary policy. A sudden demand that all banks increase their reserves would be extremely disruptive and difficult to comply with, while loosening requirements too much would create a danger of banks being unable to meet the demand for withdrawals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?