| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Prices are the messengers in a market economy , conveying information about conditions of demand and supply. Inflation blurs those price messages. Inflation means that price signals are perceived more vaguely, like a radio program received with a lot of static. If the static becomes severe, it is hard to tell what is happening.
In Israel, when inflation accelerated to an annual rate of 500% in 1985, some stores stopped posting prices directly on items, since they would have had to put new labels on the items or shelves every few days to reflect inflation. Instead, a shopper just took items from a shelf and went up to the checkout register to find out the price for that day. Obviously, this situation makes comparing prices and shopping for the best deal rather difficult. When the levels and changes of prices become uncertain, businesses and individuals find it harder to react to economic signals. In a world where inflation is at a high rate, but bouncing up and down to some extent, does a higher price of a good mean that inflation has risen, or that supply of that good has decreased, or that demand for that good has increased? Should a buyer of the good take the higher prices as an economic hint to start substituting other products—or have the prices of the substitutes risen by an equal amount? Should a seller of the good take a higher price as a reason to increase production—or is the higher price only a sign of a general inflation in which the prices of all inputs to production are rising as well? The true story will presumably become clear over time, but at a given moment, who can say?
High and variable inflation means that the incentives in the economy to adjust in response to changes in prices are weaker. Markets will adjust toward their equilibrium prices and quantities more erratically and slowly, and many individual markets will experience a greater chance of surpluses and shortages .
Inflation can make long-term planning difficult. In discussing unintended redistributions , we considered the case of someone trying to plan for retirement with a pension that is fixed in nominal terms and a high rate of inflation. Similar problems arise for all people trying to save for retirement, because they must consider what their money will really buy several decades in the future when the rate of future inflation cannot be known with certainty.
Inflation, especially at moderate or high levels, will pose substantial planning problems for businesses, too. A firm can make money from inflation—for example, by paying bills and wages as late as possible so that it can pay in inflated dollars, while collecting revenues as soon as possible. A firm can also suffer losses from inflation, as in the case of a retail business that gets stuck holding too much cash, only to see the value of that cash eroded by inflation. But when a business spends its time focusing on how to profit by inflation, or at least how to avoid suffering from it, an inevitable tradeoff strikes: less time is spent on improving products and services or on figuring out how to make existing products and services more cheaply. An economy with high inflation rewards businesses that have found clever ways of profiting from inflation, which are not necessarily the businesses that excel at productivity, innovation, or quality of service.
In the short term, low or moderate levels of inflation may not pose an overwhelming difficulty for business planning, because costs of doing business and sales revenues may rise at similar rates. If, however, inflation varies substantially over the short or medium term, then it may make sense for businesses to stick to shorter-term strategies. The evidence as to whether relatively low rates of inflation reduce productivity is controversial among economists. There is some evidence that if inflation can be held to moderate levels of less than 3% per year, it need not prevent a nation’s real economy from growing at a healthy pace. For some countries that have experienced hyperinflation of several thousand percent per year, an annual inflation rate of 20–30% may feel basically the same as zero. However, several economists have pointed to the suggestive fact that when U.S. inflation heated up in the early 1970s—to 10%—U.S. growth in productivity slowed down, and when inflation slowed down in the 1980s, productivity edged up again not long thereafter, as shown in [link] .
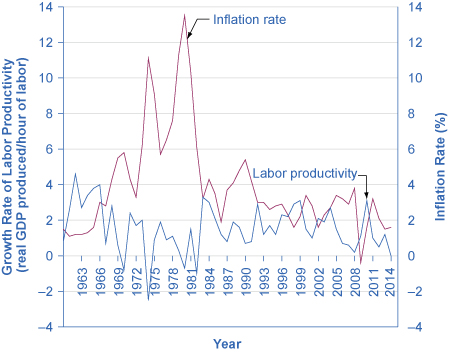
Although the economic effects of inflation are primarily negative, two countervailing points are worth noting. First, the impact of inflation will differ considerably according to whether it is creeping up slowly at 0% to 2% per year, galloping along at 10% to 20% per year, or racing to the point of hyperinflation at, say, 40% per month. Hyperinflation can rip an economy and a society apart. An annual inflation rate of 2%, 3%, or 4%, however, is a long way from a national crisis. Low inflation is also better than deflation which occurs with severe recessions.
Second, an argument is sometimes made that moderate inflation may help the economy by making wages in labor markets more flexible. The discussion in Unemployment pointed out that wages tend to be sticky in their downward movements and that unemployment can result. A little inflation could nibble away at real wages, and thus help real wages to decline if necessary. In this way, even if a moderate or high rate of inflation may act as sand in the gears of the economy, perhaps a low rate of inflation serves as oil for the gears of the labor market. This argument is controversial. A full analysis would have to take all the effects of inflation into account. It does, however, offer another reason to believe that, all things considered, very low rates of inflation may not be especially harmful.
Unexpected inflation will tend to hurt those whose money received, in terms of wages and interest payments, does not rise with inflation. In contrast, inflation can help those who owe money that can be paid in less valuable, inflated dollars. Low rates of inflation have relatively little economic impact over the short term. Over the medium and the long term, even low rates of inflation can complicate future planning. High rates of inflation can muddle price signals in the short term and prevent market forces from operating efficiently, and can vastly complicate long-term savings and investment decisions.
Shiller, Robert. “Why Do People Dislike Inflation?” NBER Working Paper Series, National Bureau of Economic Research , p. 52. 1996.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?