| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
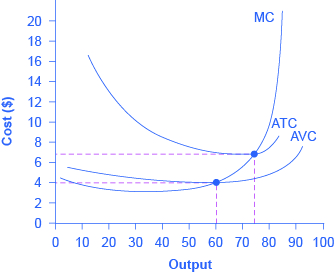
The breakdown of total costs into fixed and variable costs can provide a basis for other insights as well. The first five columns of [link] duplicate the previous table, but the last three columns show average total costs, average variable costs, and marginal costs. These new measures analyze costs on a per-unit (rather than a total) basis and are reflected in the curves shown in [link] .
| Labor | Quantity | Fixed Cost | Variable Cost | Total Cost | Marginal Cost | Average Total Cost | Average Variable Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | $160 | $80 | $240 | $5.00 | $15.00 | $5.00 |
| 2 | 40 | $160 | $160 | $320 | $3.30 | $8.00 | $4.00 |
| 3 | 60 | $160 | $240 | $400 | $4.00 | $6.60 | $4.00 |
| 4 | 72 | $160 | $320 | $480 | $6.60 | $6.60 | $4.40 |
| 5 | 80 | $160 | $400 | $560 | $10.00 | $7.00 | $5.00 |
| 6 | 84 | $160 | $480 | $640 | $20.00 | $7.60 | $5.70 |
Average total cost (sometimes referred to simply as average cost) is total cost divided by the quantity of output. Since the total cost of producing 40 haircuts is $320, the average total cost for producing each of 40 haircuts is $320/40, or $8 per haircut. Average cost curves are typically U-shaped, as [link] shows. Average total cost starts off relatively high, because at low levels of output total costs are dominated by the fixed cost; mathematically, the denominator is so small that average total cost is large. Average total cost then declines, as the fixed costs are spread over an increasing quantity of output. In the average cost calculation, the rise in the numerator of total costs is relatively small compared to the rise in the denominator of quantity produced. But as output expands still further, the average cost begins to rise. At the right side of the average cost curve, total costs begin rising more rapidly as diminishing returns kick in.
Average variable cost obtained when variable cost is divided by quantity of output. For example, the variable cost of producing 80 haircuts is $400, so the average variable cost is $400/80, or $5 per haircut. Note that at any level of output, the average variable cost curve will always lie below the curve for average total cost, as shown in [link] . The reason is that average total cost includes average variable cost and average fixed cost. Thus, for Q = 80 haircuts, the average total cost is $8 per haircut, while the average variable cost is $5 per haircut. However, as output grows, fixed costs become relatively less important (since they do not rise with output), so average variable cost sneaks closer to average cost.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?