| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The national economies that make up the global economy are remarkably diverse. Let us use one key indicator of the standard of living, GDP per capita , to quantify this diversity. You will quickly see that quantifying this diversity is fraught with challenges and limitations. As explained in The Macroeconomic Perspective , we must consider using purchasing power parity or “international dollars” to convert average incomes into comparable units. Purchasing power parity, as formally defined in Exchange Rates and International Capital Flows , takes into account the fact that prices of the same good are different across countries.
The Macroeconomic Perspective explained how to measure GDP, the challenges of using GDP to compare standards of living, and the difficulty of confusing economic size with distribution. In China's case, for example, China ranks as the second largest global economy, second to only the United States, with Japan being third. But, when we take China's GDP of $9.2 trillion and divide it by its population of 1.4 billion, then the per capita GDP is only $6,900, which is significantly lower than that of Japan, at $38,500, and that of the United States, at $52,800. Measurement issues aside, it’s worth repeating that the goal, then, is to not only increase GDP, but to strive toward increased GDP per capita to increase overall standards of living for individuals. As we have learned from Economic Growth , this can be achieved at the national level by designing policies that increase worker productivity, deepen capital, and advance technology.
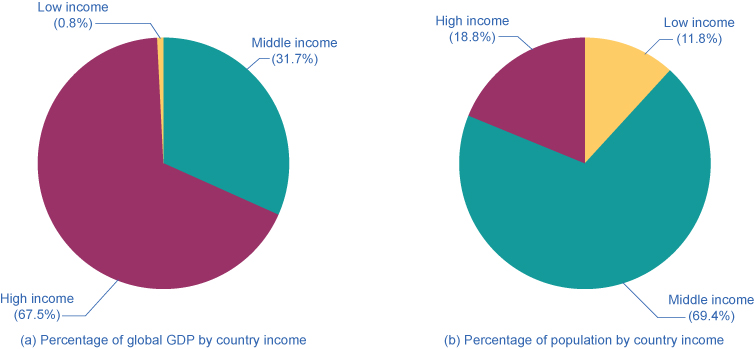
GDP per capita also allows us to rank countries into high-, middle-, or low-income groups. Low-income countries are those with $1,025 per capita GDP per year; middle-income countries have a per capita GDP between $1,025 and $12,475; while high-income countries have over $12,475 per year per capita income. As seen in [link] and [link] , high-income countries earn 68% of world income, but represent just 12% of the global population. Low-income countries earn 1% of total world income, but represent 18.5% of global population.
| Ranking based on GDP/capita | GDP (in billions) | % of Global GDP | Population | % of Global Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low income ($1,025 or less) | $612.7 | 0.8% | 848,700,000 | 11.8% |
| Middle income ($1,025 - $12,475) | $23,930 | 31.7% | 4,970,000,000 | 69.4% |
| High income (more than $12,475) | $51,090,000,000 | 67.5% | 1,306,000,000 | 18.8% |
| World Total income | $75,592,941 | 7,162,119,434 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?