| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Owls are night hunters.
Their eyes can see very well in the dark.
They hunt rats and mice
and the larger owls will even carry off chickens,
ducks and small turkeys.
Even rabbits and hares are wary of owls.
Small balls of hair are often found near their nests.
Owls swallow their prey whole and indigestible parts,
such as bones and feathers, collect inside their crops.
They are formed into small balls and are later regurgitated.
To determine what owls have eaten, scientists
and biologists will examine these small balls.
They can then say from the left-overs
what kind of animals the owl has eaten.
| LO 1.4.5 | LO 1.4.7 | LOS 2.5 | LO 3.5.1 |
For you to do.
1. Visit the library and select 3 more books about “Owls”.
Write their titles and authors’ names.
a) ………………………………………………………………………………………..
b) ………………………………………………………………………………………..
c) ………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. Choose one of these books to read.
3. Write down any new facts about owls that you have read and tell the class what you have learnt.
……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 2.7 | LO 3.3.1 | LO 3.5 | LO 4.1.1 | LO 5.3.4 |
4. Use a dictionary to find out what these words mean.
a. mottled: …………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
b. talons: …………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
c. prey: …………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
d. wary: ……………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
e. indigestible: …………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
f. regurgitate: ……………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
g. scientist: ………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
h. biologist: ………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 4.5.4 | LO 4.6.3 |
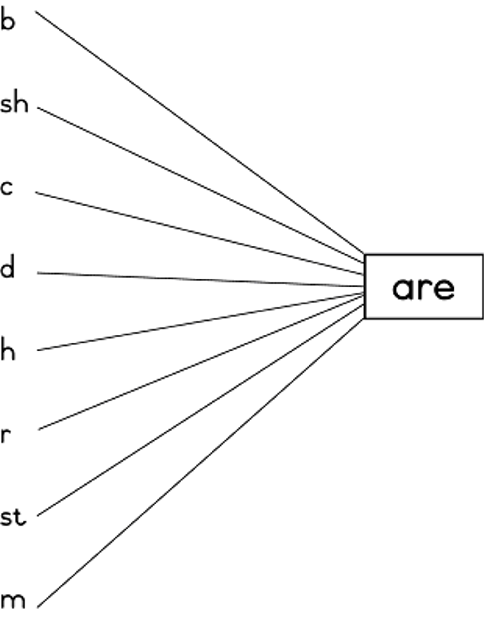
……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 3.4.5 |

| LO 4.7.1 |
Do you still remember the alphabet?
A B C . . . . . . . etc.
1. owl; bird; creature; prey.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. beak; talons; razor; eyes.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
3. rats; mice; chickens; ducks.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
4. swallow; balls; catch; examine.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
5. feathers; bones; nests; crops.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
6. regurgitate; collect; eaten; found.
…………………………………………………………………………………………..
| LO 3.5 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING : The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner listens with enjoyment to stories, poems, songs and other oral texts and shows understanding:
1.4.5 answers questions about the oral text;
1.4.7 works out cause and effect in the oral text;
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.5: We know this when the learner contributes to group and class discussions;
Assessment Standard 2.7: We know this when the learner makes oral presentations (e.g. on given topics, on interviews conducted, reporting back from fieldtrips);
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner reads texts alone, and uses a variety of strategies to make meaning:
3.3.1 reads a printed text fluently and with understanding;
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner consolidates phonic knowledge:
3.4.5 recognises vowels with two sounds;
Assessment Standard 3.5: We know this when the learner reads reads for information and enjoyment;
3.5.1 chooses fiction and non-fiction books and says what was liked or not liked about them;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner uses pre-writing strategies to initiate writing:
4.1.1 uses various pre-writing strategies to gather information and choose a topic (e.g. brainstorming, free writing, talking with friends, visual images);
Assessment Standard 4.7: We know this when the learner writes legibly:
4.7.1 writes with ease and increasing speed as a result of frequent practice;
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.3: We know this when the learner uses language to investigate and explore:
5.3.4 uses simple strategies for getting information.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 3' conversation and receive update notifications?